Is your small business in need of a contact center or a call center? It can be hard to decipher which is best for your business, especially when these terms can be used interchangeably.
Both of these services play a large part in a small business’s customer service capabilities. In order to make sure that your customers are being taken care of in the most efficient way, we have broken down the differences between a contact center and a call center so that you can confidently make the best decision for your business needs.
Today, we’ll cover:
- What a call center is
- What a contact center is
- The 3 main differences between contact centers and call centers
- Bonus: How different industries use contact centers today
🔑 What’s the key to building a strong customer-centric team? Grab our eBook to find out.
What is a call center?
A call center is a customer service operation that provides support for sales and service teams through outbound or inbound calling. Outbound calling is when the call center is making a call out to the customer. Inbound is when a customer calls in to the call center. The most important aspect of a call center is that it only offers phone support. Call centers do not offer services via other channels, such as email or text chat.
Some call centers are inbound-only or outbound-only, while others are blended. Call center services may be outsourced or in-house. In either case, call center agents either work on physical premises or remotely.
Inbound agents handle questions, complaints, technical support, and payment of bills. Outbound calls are used for telemarketing, appointment reminders, payment collection, customer surveys, and fundraising.
Call centers may use PSTN (public switched telephone networks) or VoIP (voice over internet protocol) telephony to make and receive voice calls. They can usually handle high volumes of incoming calls, with the ability to place callers on hold and answer inquiries according to queue position.
Smart call center software like RingCX includes automation such as ACD (automatic call distributors), smart routing, and predictive dialers. Call centers also need analytics to measure various KPIs (key performance indicators), from first-call resolution to average handling time and customer satisfaction.
If your particular industry or customer base largely prefers phone calls, a traditional call center may suit your needs. But if you want to give customers more communication channels, you might want to upgrade to a modern contact center.
What is a contact center?
A contact center is a lot more than phones, although that is still a big piece of the puzzle for most businesses. Contact centers field customer interactions on all sorts of other channels: email, live chat, even social media. Depending on the integration, they can either be a multichannel or omnichannel service (what’s the difference?). Like call centers, they can be in-house or outsourced.
These days, customers expect to reach companies on a variety of digital channels for speed and convenience (49% use three to five different channels to contact customer service1).
Alongside phone channels, contact centers handle inbound and outbound interactions via email, live chat, messaging, social media, video, and even fax.
Customers might choose chat for non-urgent inquiries, email for more detail, and phone for complex issues. In multichannel centers, the conversations on different channels are largely siloed, whereas omnichannel centers have all interactions unified in one interface.
Omnichannel contact centers use intelligent routing so that customers can move seamlessly across channels during the same interaction, and the entire customer journey is visible. This requires coordination and integration of people, processes, and technology across the business.
Contact centers need to add extra metrics to evaluate performance. You can set targets for response times to inquiries and measure first contact resolution and cost per contact by channel.
Contact centers typically involve automated self-service options like chatbots and IVR (interactive voice response), too, to help customers resolve issues faster. Contact center software (such as RingCX) is often cloud-based, with the added benefits of scalability and reduced costs. Here’s a look at how RingCX works:
3 main differences between a contact center and call center
Besides the big differentiator between a contact center and a call center—which is that a call center only uses a phone while a contact center can use multiple channels—there are three more notable differences between the two:
1. Self-service
Contact centers are able to provide self-service capabilities, which is incredibly important in this “do it yourself” trend that we are seeing across the board. It is possible for call centers to offer this service, but generally call centers will stick to voice calls.
Self-service can be a great time-saver, as it enables customers to solve issues themselves and avoid long wait times. They can access FAQs, knowledge bases, or video tutorials, while software providers like RingCentral offer advanced speech analytics so that bots recognize and respond to common queries. This is known as interactive voice response, or IVR. Here’s a sample IVR flow:
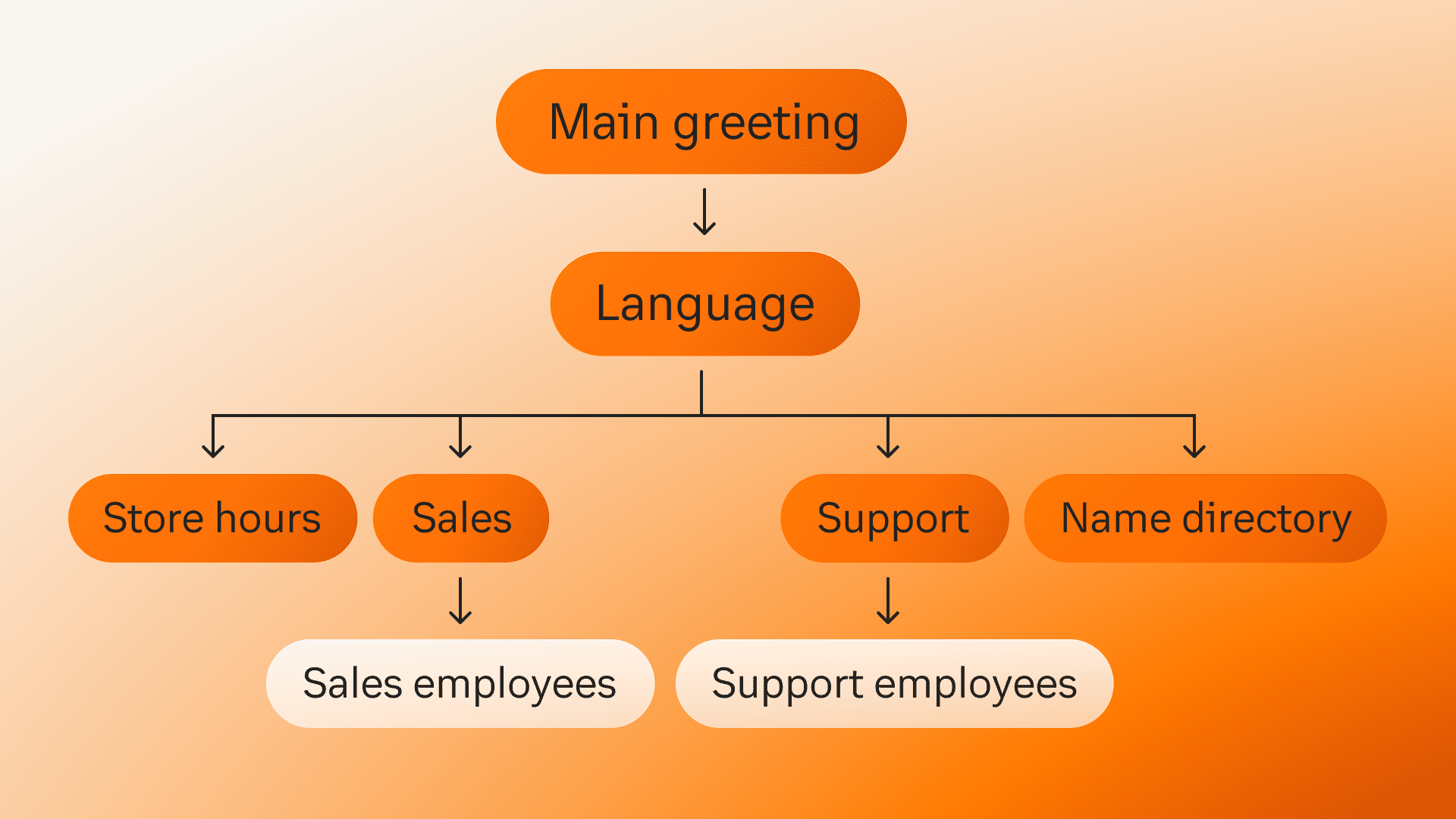
Self-service is also a winner for agents, as it weeds out interactions that don’t require human input and keeps inbound call volume down. They can then spend more time on more complex interactions that do need a personal touch—leading to improved productivity as well as customer happiness.
If a chatbot or IVR doesn’t have the answers, it will pass the customer to a human agent. In an omnichannel center, all the information should transfer with them so they don’t have to start from scratch. Mobile apps should include this functionality.
Combined with human intervention, self-service helps you to offer more comprehensive support. 63% of contact center leaders agree that virtual assistants and chatbots make it easier for customers to have their issues resolved.2
2. Employee growth
A call center needs to be staffed with capable and trustworthy agents that are able to troubleshoot any problem that may arise. This can allow for a more “one on one” relationship with customers, as the company is taking the time to provide them with an actual person to walk through their problem with them.
While call center staff need to demonstrate good listening and empathy, contact center agents need some extra skills on top. Because they’ll interact with customers via text message, chat, and email, they have to be good at written communication, too.
That means clear, concise responses to avoid misunderstandings and the ability to “read between the lines” without hearing the customer’s tone of voice (RingCX’s AI-powered features can also help you detect how the customer is feeling). Agents must be aware of social media etiquette—you can’t afford the negative publicity of a Twitter spat.

Multitasking is another skill required by contact center employees, as they deal with several inquiries simultaneously. They need to handle both inbound and outbound interactions on all channels and meet customer expectations by responding in the optimum time.
Contact centers will probably need extra staffing and training to cover a wider range of interactions. Center managers can use performance management and coaching tools to ensure that all agents are confident in using contact center technology.
Cloud contact centers and call centers make it easier for agents to work from anywhere, and the operation is fully scalable—vendors like RingCentral can provision new users in minutes, while subscription-based pricing means centers can scale up or down according to demand.
3. Customer experience
Call centers are traditional and were the norm before contact centers arrived on the scene. Call centers have been proven to boost customer experience by providing a human touch, but contact centers also offer plenty of scope for personalized customer communications.
One key difference is that contact centers generate more customer data, which should be used not just for evaluating performance but also to build better relationships with customers. Data lets you learn more about customer preferences and behaviors, helping you to personalize future interactions. More channels = more data!
Contact center solutions like RingCX house all conversations in one place so that nothing gets lost. When agents store data in a CRM (customer relationship management) system, they can access this during any customer interaction and instantly view the info they need to enhance the overall experience.
Analytics and reporting tools are also important aspects of a contact center, as they harness this extra data to highlight areas for improvement. But in both call centers and contact centers, measuring metrics is essential for delivering a consistently great customer experience.
As we mentioned earlier, customers enjoy the extra convenience brought by omnichannel cloud contact centers, with the freedom to choose their preferred channel. 89% of customers are retained by companies with strong omnichannel customer engagement.3
How do different industries use contact centers?
Many industries can benefit from using a contact center or a call center. In fact, any business that interacts regularly with customers—or wants to improve its communications—should consider a customer support center.
Banking
With fewer physical branches, many customers have to contact their banks remotely. And when it comes to money matters, they don’t want to wait—especially if there’s a problem. Contact centers allow banks to engage rapidly and securely with clients and to access real-time customer information.
Energy and utilities
In this industry, contact centers typically handle customer inquiries and collect payments. SMS messages are also handy for sending billing reminders, warnings of service outages, and suggestions like “save water by turning off your sprinklers during a rainstorm.”
Government
Government contact centers help citizens find essential information and make officials more accessible, as well as being used for canvassing and surveys. Obviously, all conversations must be secure, which is why RingCentral’s solution offers government-compliant infrastructure and seven layers of security.
Healthcare
Security is also essential for healthcare contact centers. Agents may send out appointment reminders and instructions, give patients their test results, and handle Medicare inquiries or payments. Omnichannel support can also include video consultations and webinars for medical device training.
Insurance
Insurance firms use contact centers to sell (or upsell) their services, remind clients about renewals, and collect payments. With the right software, they can also send out policy documents and talk through them online via video and screen sharing.
Retail
Both online and brick-and-mortar retailers handle plenty of inquiries, with customers checking that items are in stock or setting up returns. Contact centers can quickly connect them to the right department, as well as sending SMS alerts for deliveries or in-store collection.
Telecommunications
If you’re running a telecommunications business, you need to practise what you preach with a great communications system of your own, including a contact center with smart tools like auto call distribution and callback. Agents will handle sales, setup of systems and products, and technical support.
Travel and hospitality
These contact centers need to handle reservations, answer queries, deal with suppliers, and send notifications about travel delays and takeout deliveries. If you’re running a pop-up outlet or food truck, a cloud-based system keeps you in touch with customers on any mobile device, anywhere.
Human resources
Contact centers are essential for human resources, with agents taking inquiries and providing information about workplace health and safety, salaries, annual leave, and employee grievances.
Contact center or call center: Which one is best for your business?
It depends on your business and the resources you have, but an omnichannel contact center offers more choice, convenience, and opportunities for customer engagement. But remember that a reliable phone system is still a vital tool in customer support.
Whichever type of center you choose, you have to deliver a great experience that meets customer needs. Automated systems and unified communications are the best way to do this.
Ready to get started? Check out the AI-powered RingCX contact center for your business.
Originally published Jan 18, 2024, updated Jul 23, 2024





