If you’re still using on-premises IT infrastructure, your business is missing out on the benefits of cloud communications and computing. The key challenge is migrating applications and systems with minimal business disruption.
Enter Kubernetes, an open-source platform that supports your cloud migration strategy by making it easier to deploy, scale, and maintain containerized apps in the cloud.
In this post, we’ll explain what all of that means for your business—and show you the steps involved in making it happen.
What is a cloud migration strategy?
Cloud migration is the process of moving all your digital assets—such as applications, databases, and IT resources—from an on-premises system to a cloud platform or moving them from one cloud to another.
A cloud migration strategy is the roadmap for a smooth transition. It is often part of a company’s wider digital transformation plan. A robust strategy will help reduce the risk of downtime and ensure that the migration is in line with business goals.
What are the benefits of cloud migration?
Cloud migration benefits businesses in many ways, as the move away from on-premises legacy systems brings increased efficiency and reduced costs. With your digital assets stored in the cloud, you won’t need to house or maintain any physical infrastructure.
Cloud computing is fully scalable, with dynamic resource utilization and pay-as-you-go pricing models. It makes your systems and apps accessible from anywhere while keeping them secure. Migration is a way to future-proof your business and remain competitive in the digital age.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform for businesses to deploy apps, systems, or software on cloud architectures. It’s designed to manage and scale containerized cloud applications.
What do we mean by that? The rise of cloud computing and server virtualization has made it possible to implement more flexible deployment architectures, using containers to package and distribute apps and services.
Containerization breaks software into smaller components, making it easier to scale applications. Kubernetes has become the standard for managing (or “orchestrating”) these containers, and many businesses now include containerization in their cloud migration plan.

How does Kubernetes support cloud migration?
Kubernetes is a perfect partner for cloud computing, as both involve improving scalability and flexibility. Here are some of the benefits:
Simplifies the migration process
Kubernetes gives you the flexibility to deploy both cloud-native and legacy applications, so you can implement the migration in stages over time—simplifying the process and reducing the risk of problems.
If you’re planning to take advantage of emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and big data analytics, Kubernetes also simplifies their integration into your tech stack.
Encourages cloud-native apps
Through its use of containers, Kubernetes supports the adoption of cloud-native applications. Cloud-native apps are designed to leverage cloud technologies, connecting to cloud services and extending your system’s capabilities without a lot of coding.
Cloud-native application examples include APIs and software containers. They’re based on microservices—small, self-sufficient mini-programs for executing single business functions—which means you can scale individual services without affecting the entire system.
You can also build and update them quickly and run them in any cloud environment, providing a consistent experience. This streamlines the development, release, and deployment processes, fostering innovation and fast responses to changing markets and technologies.
Automates scalability
With cloud migration, you’ll need to handle changeable workloads and scale your operations quickly. Kubernetes automates scaling processes for apps and services, ensuring that applications run smoothly during peak usage.
For example, if you’re embracing an AI virtual assistant, you’ll need more resources available for fine tuning large language models (LLMs).
Kubernetes supports both horizontal scaling—adding or removing containers based on demand—and vertical scaling, adjusting the CPU and memory limits of your containers.
This enables you to deploy resource-heavy elements like AI/ML models and data processing pipelines.
Optimizes resources
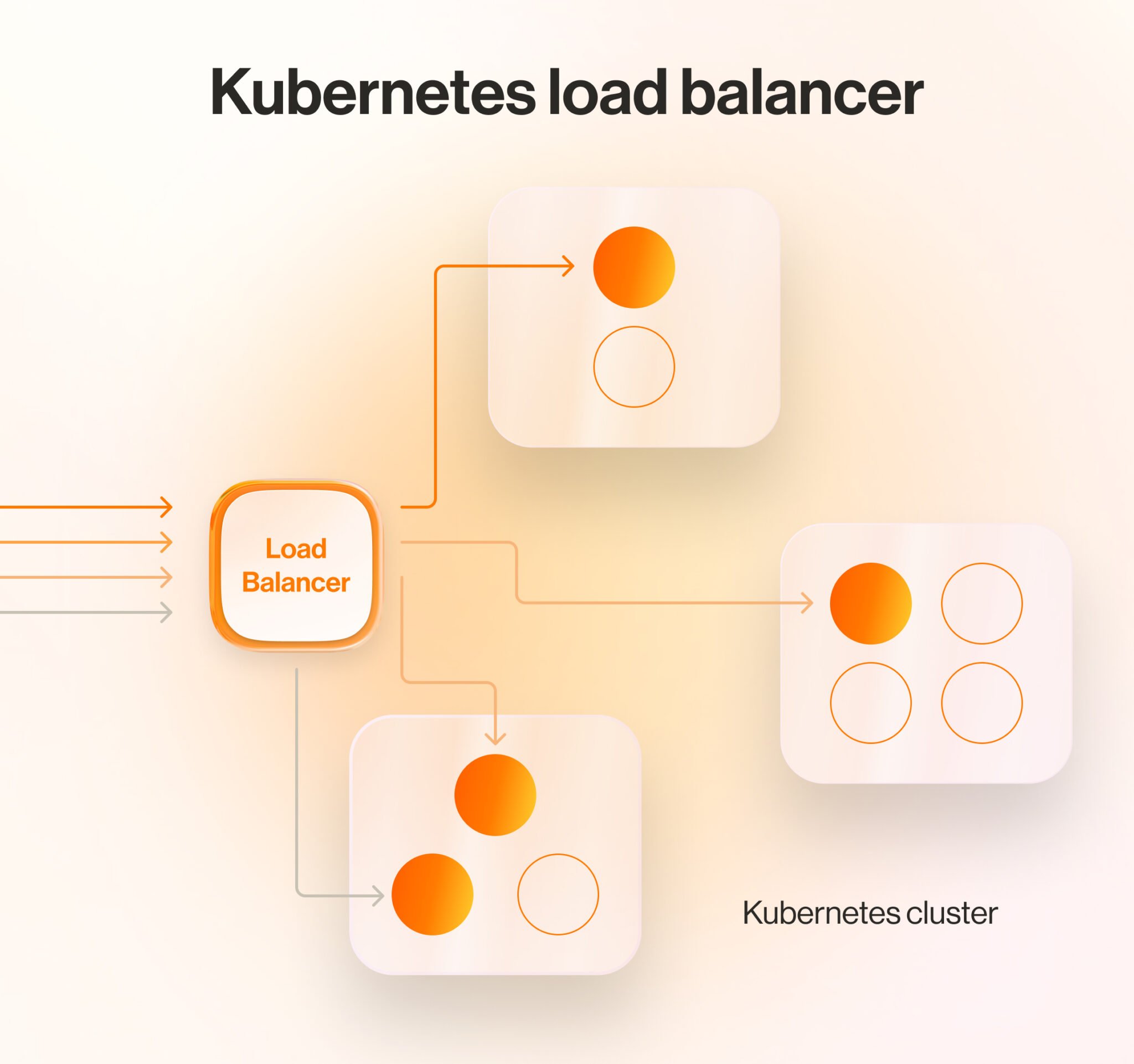
By automatically allocating computing resources based on your actual needs, Kubernetes optimizes resource utilization during the cloud migration process.
This automated load balancing makes for efficient resource management, giving apps the required resources while minimizing waste.
It brings further efficiency by optimizing cloud infrastructure resources and reducing ecosystem maintenance costs.
For instance, autoscaling means that your IT team can manually tune the CPU, RAM, and storage for pods. Overall, you’ll have more money left to spend on innovation.
Monitors and fixes issues
Kubernetes monitors the health of your applications and systems during and after migration, minimizing the risk of downtime. It will automatically restart, replace, or reschedule containers in the event of failure so there’s no disruption for users.
It also lets you make changes to apps without experiencing downtime and even roll back to previous versions in case of errors or failures. This means you can quickly update your services in response to evolving requirements and user feedback.
Provides flexibility
Kubernetes itself is highly flexible. You can run it on a number of cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure, and it’s portable across infrastructure.
Cloud-native applications are also more adaptable, so you can choose to use them on the private, public, or hybrid cloud—or in multi-cloud environments to reduce vendor lock-in.
How to use Kubernetes to scale your cloud migration strategy
It’s important to take a structured approach to cloud migration, so here’s a step-by-step guide for using Kubernetes to scale your strategy.
1. Understand Kubernetes
Before you proceed, make sure that you understand how Kubernetes works and what it can do for your business systems regarding cloud migration.
Be clear about what you want to get from it, and look into the potential downsides or challenges.
You should also fully understand your current environment, infrastructure, applications, and workloads and how they’ll fit into a Kubernetes environment.
If you need advice on this, working with a provider can be a great way to harness their technical expertise and reduce the load on your own IT staff.
2. Restructure your applications
It’s possible that some of your existing apps and services—for instance, legacy, stateful, or monolithic applications—won’t be compatible with Kubernetes.
To tap into the full capabilities of Kubernetes, you may need to swap monolithic virtual machine-based models for container-based ones.
This involves refactoring or rewriting apps to make them more modular and stateless, breaking them down into smaller independent services that communicate through APIs.
You’ll also need to ensure that current integrations and dependencies with other systems and platforms will still work effectively under Kubernetes.
3. Choose a cloud platform
As we mentioned earlier, one benefit of Kubernetes is that it works across all cloud environments, so the choice is yours.
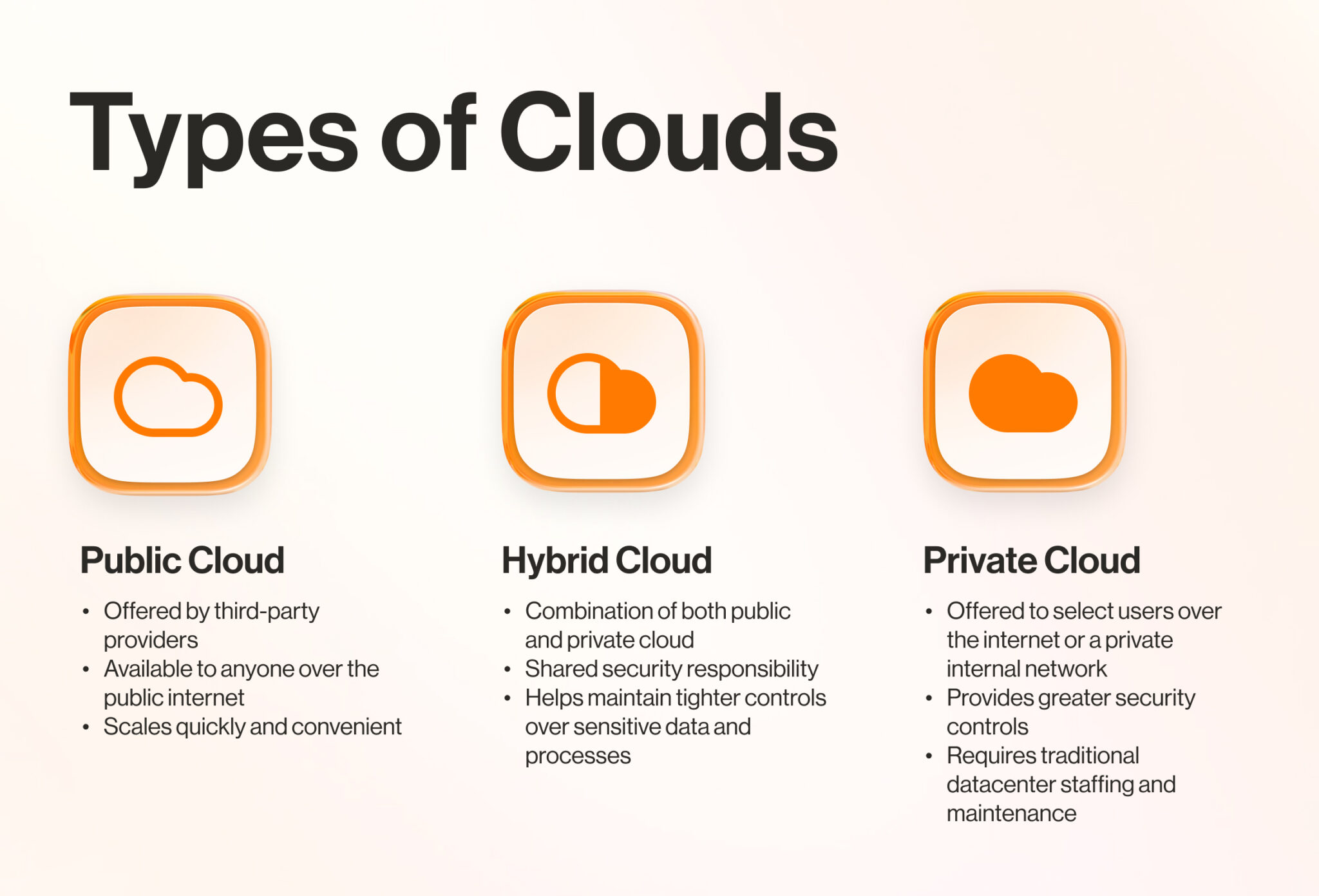
- In a public cloud, the infrastructure and services are in the hands of a third-party vendor. You share the hardware, storage, and network devices with other cloud “tenants” and access your own account via the Internet. This results in lower costs and greater scalability.
- A private cloud solution, either located at your on-premises data center or hosted by a third-party provider, maintains services and infrastructure on a private network, and your business has exclusive access to the hardware and software. It’s flexible and gives you more control.
- Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds or on-premises infrastructure with the public cloud. Users can move data and apps between the two environments and enjoy the advantages of both cloud types.
If you want to take advantage of more than one cloud type, Kubernetes also runs on multi-cloud environments where you use services from more than one public cloud vendor at the same time.
4. Create a Kubernetes cluster
A Kubernetes cluster is typically a network of physical and/or virtual machines that work together to run an app. The next step is to create a cluster on your cloud platform and configure it to meet your specific requirements. You can do this with a tool like Kompose or Terraform.
If that seems a bit beyond your technical capabilities, don’t worry—with a managed Kubernetes platform, you should be able to set up a cluster via your provider.
5. Deploy containers
Now, you can create your containers and then deploy them on your Kubernetes cluster. This involves building container images, which are ready-to-run software packages that contain everything needed to run an application, such as code and application and system libraries.
Various tools are available to help you create containers, including Docker. Again, if you need help with this, a managed solution can help.
6. Test your applications
It’s time to test your apps and services on Kubernetes to make sure they work properly before you go live with the cloud migration project. There are various types of tests:
- Unit testing: checks individual components or functions of a microservice
- End-to-end testing: simulates user workflows to make sure the application functions properly for end users
- Integration testing: verifies that different components work together as expected
- Load or performance testing: evaluates the app’s ability to handle load and maintain responsiveness under various conditions
- Resilience or chaos testing: checks that the app is able to recover from failures
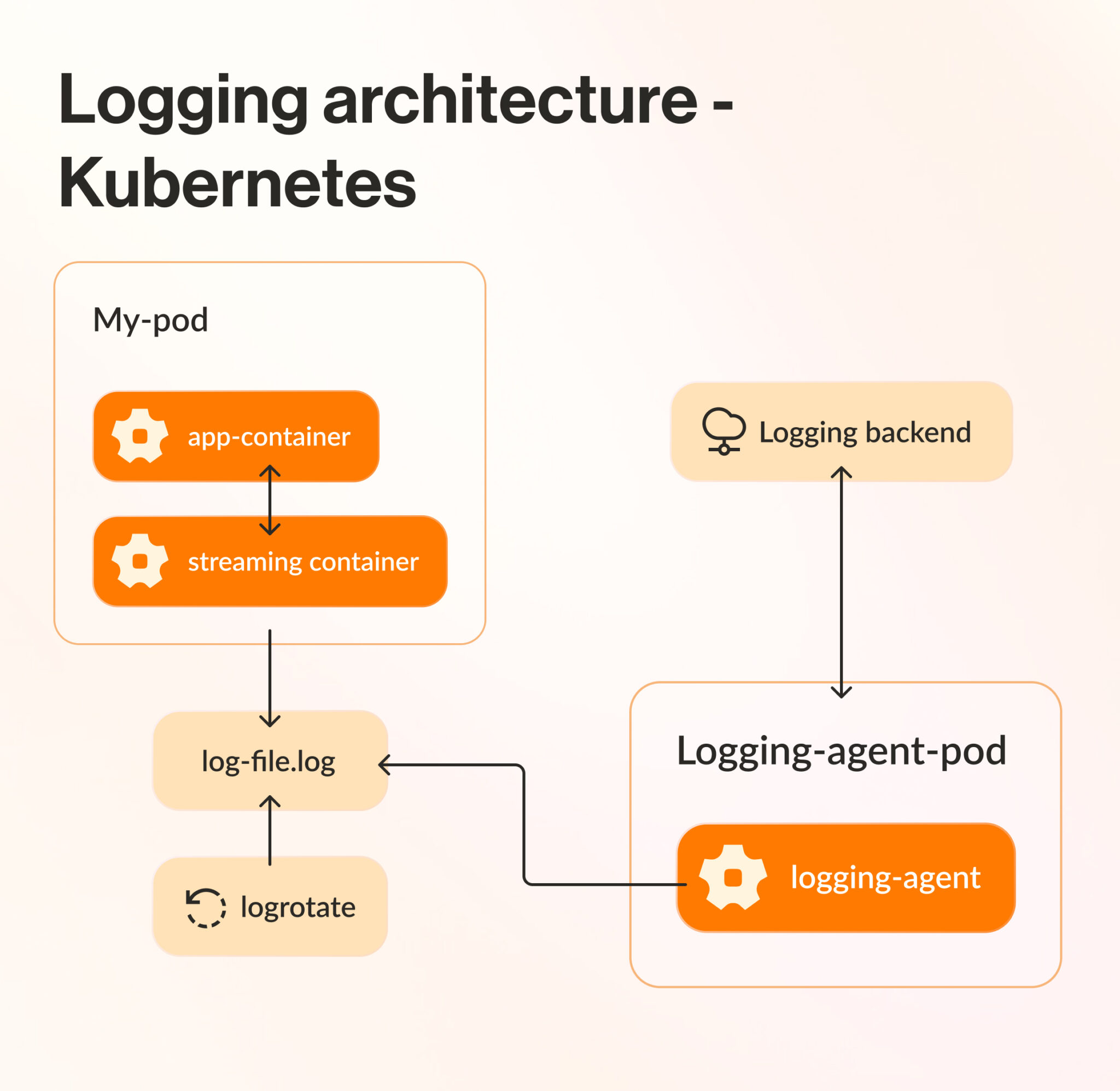
7. Use monitoring and logging
By keeping an eye on what’s happening inside your Kubernetes cluster and by having clear communication channels, you can quickly identify problems, alert the right team, and promptly resolve any issues.
This means you can minimize downtime and check for anything that could derail the migration. Set up your system to collect logs from various sources, aggregate them, and store them centrally for analysis.
Best practices
Here are a couple of extra tips to help the Kubernetes-based cloud migration go smoothly.
Consider security
Managed Kubernetes platforms come with built-in security, but there are still things you can do to minimize potential risks as you migrate to the cloud.
Common security measures include using role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to the Kubernetes API server and resources and using Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure the communication between the Kubernetes API server and the nodes, pods, and services.
Provide training
Kubernetes is a complex system, so make sure your team has a sound understanding of basic and advanced concepts. Kubernetes certifications can help to enhance their technical expertise.
They’ll also need ongoing training to stay up-to-date with changing technology and security requirements. This includes your customer support team, who may need to answer queries about the new setup.
Communicate your plans
A lack of communication can create real difficulties when rolling out any new system.
So, let everyone in the organization know about your migration, the benefits it will bring, and how you’re using Kubernetes to facilitate it. This includes stakeholders, as buy-in from them is crucial for a successful cloud migration.
Final thoughts
As we’ve seen, pairing Kubernetes with a cloud migration strategy offers multiple benefits. It helps you to scale your efforts while reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency—and enables your business to be agile in the face of change.
Kubernetes gives you the necessary tools to modernize your infrastructure, no matter what type of cloud platform you’re migrating to. Once you get to grips with its complexities, you’ll be able to take full advantage of its capabilities and position your business ready for the future.
FAQs
How does Kubernetes work?
Kubernetes is designed to manage containerized applications, in which the software is broken down into smaller components to make scaling easier. Containers are like individual packages that each hold a piece of software and all the elements required to run it.
The containers are organized into different levels: pods, nodes, and clusters. Pods are groups of containers, nodes are the machines that manage and execute the pods, and clusters are multiple connected nodes that work together to run the app.
What are the challenges of Kubernetes?
The main challenge is complexity, as Kubernetes has a steep learning curve. It takes time and effort to learn how to use it effectively, and it requires technical knowledge of programming, system administration, and network infrastructure.
Kubernetes also comes with certain security risks, so you need to configure it properly and use robust security measures like firewalls and encryption.
Why should I migrate to the cloud?
Cloud migration helps you to make your business operations more efficient and reduce costs. When your digital assets are hosted in the cloud instead of on your premises, the cloud service provider is responsible for ownership and maintenance.
You can access your tools and data from anywhere via the Internet, and you can scale your business without limits.
Updated Aug 03, 2025