Customer support isn’t getting any simpler. Ticket volumes are rising, customer journeys are becoming more complex, and shifting expectations around response times are placing more strain on already-stretched teams.
Simply throwing more staff at the problem won’t work. Squeezed budgets and finite team capacity means every customer interaction has to work harder to resolve issues quickly and without avoidable escalation—all while keeping customer experience (CX) front of mind.
For leaders looking to scale support without burning out agents or breaking budgets, AI self-service has moved from a nice-to-have to a necessity.
Let’s look at how AI self-service is changing day-to-day support operations and what it takes to deploy these systems in a way that actually delivers value—to you, and your customers.
AI self-service: Key takeaways
AI self-service is becoming essential to how modern support teams manage rising demand without adding unnecessary strain.
When thoughtfully designed, these tools improve the flow of support interactions, help agents work more efficiently, and give customers faster, more consistent answers.
Success depends on how well the AI self-service systems fit into existing workflows, how easily they adapt to real user needs, and whether they add value across both employee and customer experiences.
The best results come from treating AI not as a shortcut or replacement for human teams, but as a way to make support more responsive and scalable while keeping agents in the loop where it matters.
What is AI customer self-service?
AI customer self-service is a technology-driven approach to tackling basic customer support needs using artificial intelligence.
It often takes the form of a virtual assistant or automated system that interprets what the customer is trying to do and helps them reach a resolution without needing to involve a support agent.
Using AI in this way can speed up issue resolution and ease pressure on customer support teams, reducing queue backlogs and freeing up agents for other key tasks.
What about employee self-service AI?
AI self-service isn’t limited to customer-facing tools. Support teams also benefit from systems that provide guidance during live interactions with customers.
Employee-facing solutions like RingCentral RingCX AI Agent Assist provide real-time support by drawing on connected business resources and pointing agents towards a resolution as the call unfolds.
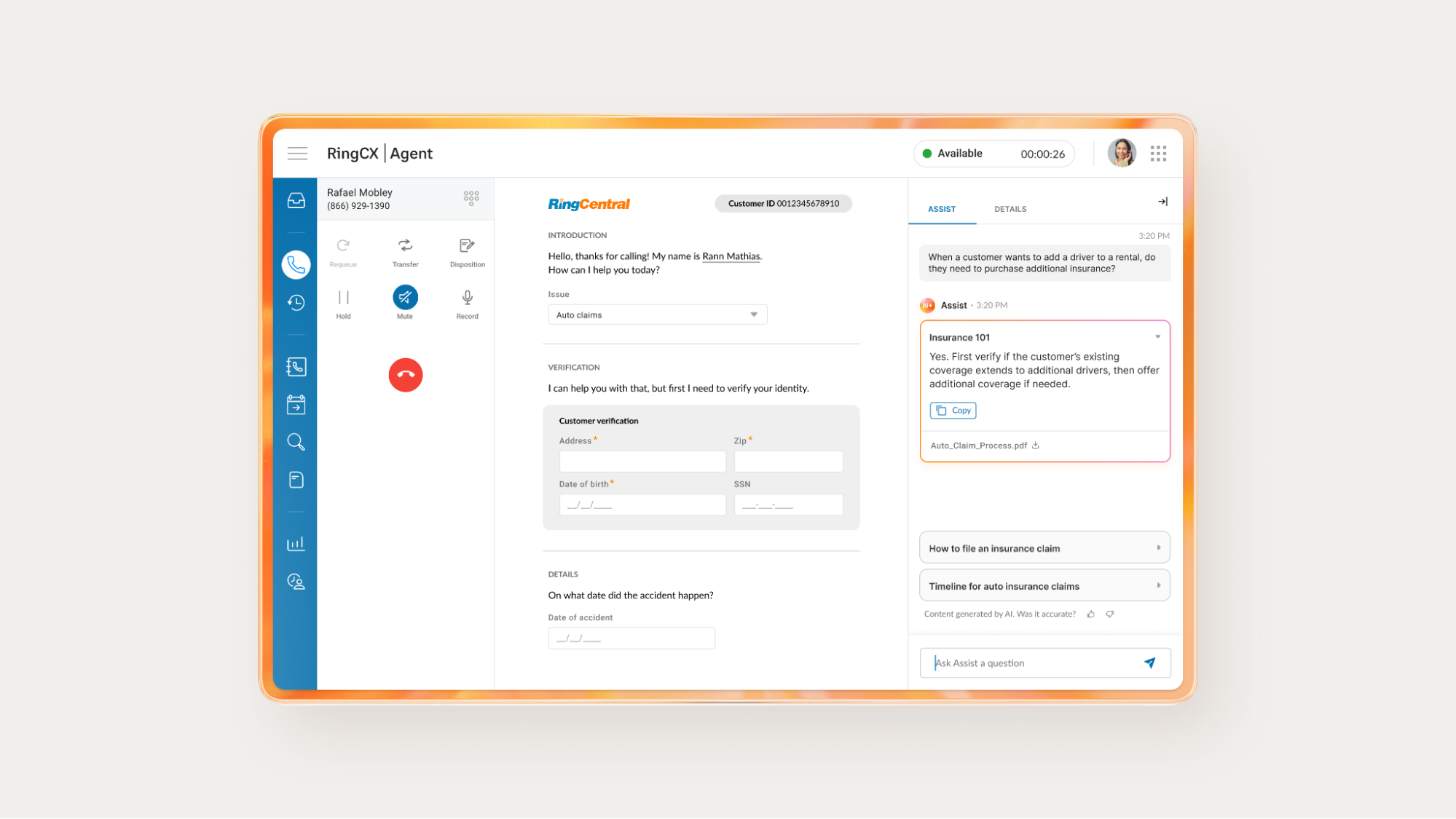
For example, when a customer asks a technical question mid-call, RingCX AI Agent Assist can instantly pull the answer from internal resources like FAQ guides and troubleshooting manuals and surface it in the agent’s workspace—no switching tabs or digging through documentation needed.
When built into the agent’s workspace, AI self service solutions can speed up decision-making and help agents resolve customer issues more efficiently, without adding complexity to their workflow.
Applications of self-service AI in contact centers and beyond
Helping both customers and staff, self-service AI is increasingly being implemented by business across industries. Here are just a few of the most useful applications of the technology:
Contact centers
Modern support centers increasingly rely on AI agents that handle routine tasks like password resets or order updates on digital platforms.
Likewise, most cellphone, internet, and utility providers nowadays offer some form of AI assistant or intelligent virtual agent within their apps and online platforms.
These tools can verify customers’ identity and guide them through troubleshooting or account management tasks within a chat interface, reducing the need for multi-step navigation and intervention.
Agents remain available, but typically only step in when an issue falls outside the AI’s capabilities, or when a customer requests direct support.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AI self-service helps manage demand more effectively and improves patient access to time-sensitive support.
Tools that guide patients through symptom checklists, appointment scheduling, referral pathways, and health screening are becoming noticeably more common in both public and private care settings.
AI self-service tools help patients find the most appropriate service or resource for their needs, reducing unnecessary appointments and easing pressure on clinical and administrative teams.
AI-powered self-service knowledge bases also improve public awareness by helping people access clear, accurate information on health and wellbeing topics, contributing to better population health outcomes.
Public services and government agencies
Government agencies and public sector organizations are increasingly using self-service AI solutions to make it easier for citizens to access key information.
These systems allow users to check the status of applications or claims, update personal information, or get step-by-step guidance on common processes without having to call or wait in line, reducing pressure on contact centers.
On the staff side, AI tools can help speed up routine work by handling straightforward inquiries more efficiently and reducing time to resolution. This can be especially useful during peak periods, like tax season, public holidays, or when there’s disruption to public services, when high demand can quickly lead to bottlenecks.
Retail
Retailers are applying AI in customer service to help customers resolve common issues on their own, particularly around post-purchase support and account-related issues.
Many retailers now offer AI-powered chat assistants that handle tasks like order tracking and returns directly within mobile apps or websites—Amazon being an obvious example.
Self-service AI also plays a key role during periods of peak demand, such as holiday sales and major product launches, helping customers get the answers they need more quickly while reducing pressure on customer service teams.
How AI self-service tools can improve the customer experience
Beyond helping organizations manage support more efficiently, AI-powered self service is changing how customers interact with service teams.
When designed and deployed with the end user in mind, AI self-service tools can make everyday tasks feel faster, smoother, and more intuitive, providing:
Faster access to help
For many customers, the biggest benefit of AI self-service is speed.
Virtual assistants and automated systems can respond instantly at any time of day, guiding users to relevant answers without needing to wait in a queue. This kind of immediate support is particularly useful for routine queries, where customers often just need quick confirmation or a simple update.
Smoother interactions
AI customer self-service tools help to streamline support journeys by removing unnecessary steps. This helps ensure customers don’t get bounced back and forth between different support teams or encounter the same information repeatedly.
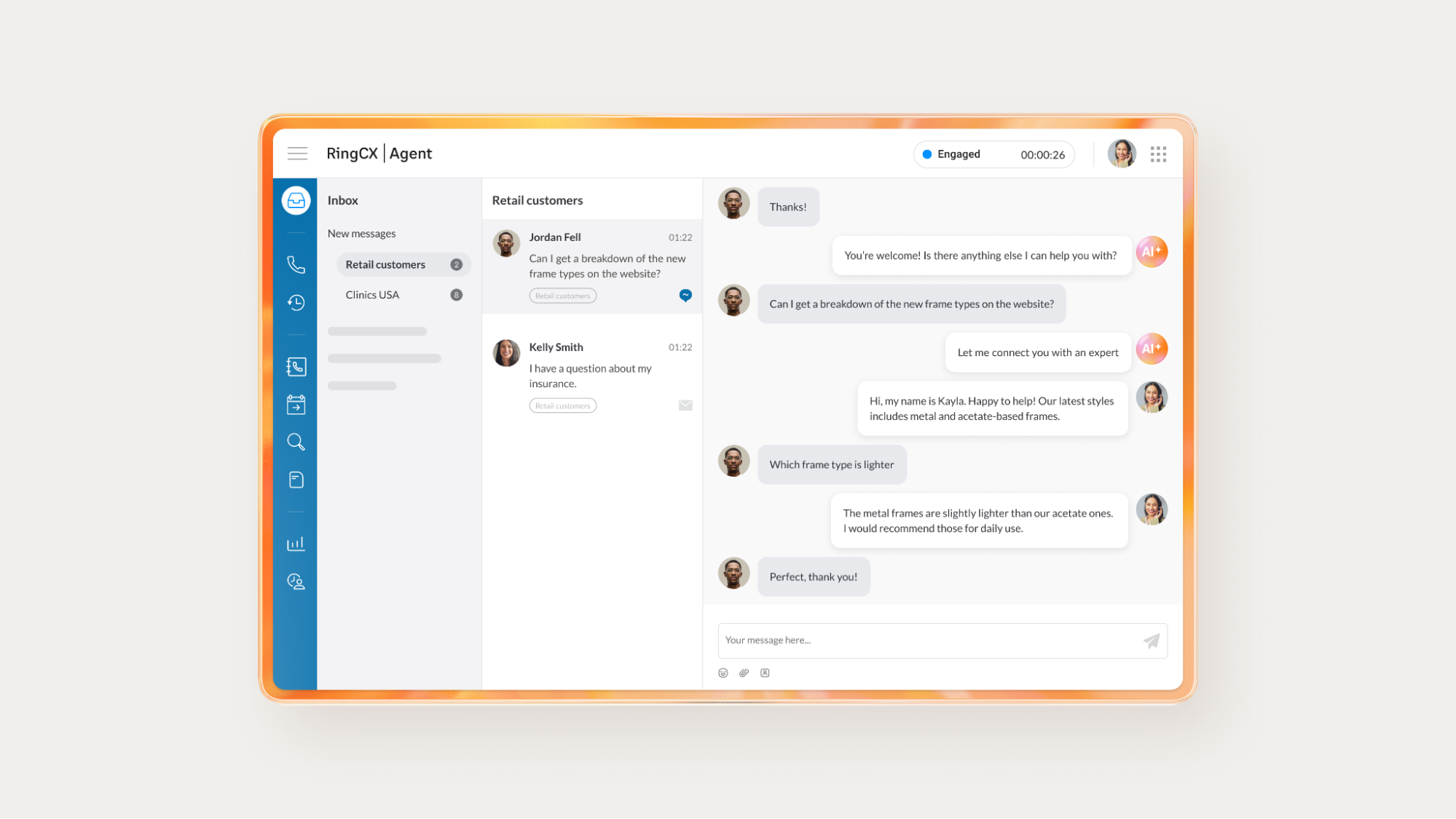
A well-integrated AI contact center solution can help you pick up where the customer left off, carry context from one channel to another, and surface the right content at the right time. That level of continuity makes the process feel more natural and less frustrating.
More consistent service
By handling common issues in a standardized way, AI self-service helps ensure customers receive clear and reliable support regardless of when or how they get in touch. It can also reduce the risk of human error on straightforward queries, which often lead to repeat contacts when mishandled.
Adaptive support
Through machine learning, AI assistants and intelligent virtual support agents learn to recognize different customer needs and preferences. This enables AI self-service tools to tailor support experiences to individual users.
Over time, these tools can learn from customer interactions and improve how they respond, whether that’s refining search results, anticipating the next step in a process, or adapting how information is presented to the user.
Challenges to overcome when using AI self-service solutions
While AI self-service can make customer support more efficient and accessible, it also introduces challenges that organizations need to manage carefully.
A key issue is accuracy. If AI tools misinterpret queries or surface the wrong information, it can frustrate users and increase support volume rather than reduce it. Ensuring systems are trained on relevant, high-quality data and regularly reviewed by human teams is essential to maintaining reliability.
Another common concern is discoverability. Customers won’t benefit from AI self-service if they don’t know it’s there, or if it’s difficult to use. Clear signposting, intuitive design, and consistent placement within apps or sites can help ensure users engage with these tools as intended.
Finally, some queries will always require human judgment or oversight. AI systems should be designed to recognize their own limits and pass queries over to agents when needed, without creating dead ends or friction in the user experience.
With the right safeguards and monitoring, AI-powered self-service can improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction without compromising trust or usability.
Best practices for implementing AI self-service software
Rolling out AI self-service tools requires more than just adding a chatbot to your app or website. The systems need to be practical, usable, and well-aligned with the way customers actually seek support. Below are a few key principles for doing it well:
Start with high-volume, low-complexity tasks
AI self-service is most effective when applied to routine queries that follow a predictable path.
Requests like checking an order status or updating delivery details are predictable and often require little judgment, but are also time-consuming for customer support teams, making them a practical starting point.
Focusing on these high-volume, low-complexity tasks first not only builds trust in AI self-service tools, but also helps organizations secure early wins that boost confidence and make a meaningful difference to support teams.
Make the experience feel seamless
Customers shouldn’t have to work hard to find and use self-service tools.
Integrating AI chatbots, virtual assistants, or intelligent automated support within existing digital touchpoints—such as apps, account dashboards, and online help centers—ensures users can easily access support when they need it.
You should also strive to keep handoff processes between AI tools and customer support agents smooth and visible in cases where a query falls outside the AI’s scope.
Use real customer interaction data to shape design
Successful AI self-service relies on understanding how customers phrase their questions and what outcomes they expect.
Use search queries, support logs, and other customer interaction data like transcripts to shape the training data and language of your AI self-service tools. This ensures the tool speaks the same language as you and your customers.
Monitor and refine continuously
AI model performance will shift over time as customer behavior changes and new queries, products, or language patterns emerge. Without regular reviews, even a well-trained model can start delivering less accurate or helpful responses.
This means it’s important to track how well your self-service tools are resolving issues. This includes identifying where users drop off and when human intervention might be needed. Use this insight to adjust responses and retrain AI models if necessary. Human oversight should always stay in the loop.
Keep human support close
Even the best AI systems will hit a wall at times. Make it easy for users to request help from a person when needed, and ensure agents have visibility into the customer’s journey so they can pick up without repeating steps. Frustration often comes not from the AI itself, but from poor transitions when it can’t help.
AI-driven self-service analytics and reporting: Measuring success
Understanding how AI self-service tools perform requires more than surface-level metrics. It’s not enough to know how many users engage with the system. What really matters is whether they get what they need, when they need it.
Resolution rate
One of the clearest signs that an AI system is doing its job is when users complete their task without needing human help.
High containment rates, where users stay within the self-service interface and reach a resolution, usually indicate that the system is easy to use and fit to task. A drop in this rate over time can indicate new user expectations, such as the need for faster responses or more personalized help, or reveal gaps in the guidance that need to be addressed.
Time to resolution
Reducing the time it takes to get something done is often one of the core goals of AI self-service.
If users are still spending several minutes or more to complete a basic action, or if they get stuck in a cycle of repeated steps, it may be time to simplify the journey or retrain how the AI model handles certain inputs.
Drop-off patterns
Drop-offs tell you where users get stuck. If customers abandon the interaction part-way through or restart the process without getting anywhere, it may indicate that prompts are unclear, the system isn’t picking up on what the user is trying to do, or logic that doesn’t match the task at hand.
Whatever the reason, these moments are valuable signals that help you spot friction and smooth out the experience.
Satisfaction scores and user feedback
Feedback from users can help flag edge cases or unexpected issues the system isn’t handling well. If people are rating their experience poorly, or frequently asking to speak to a person for even straightforward tasks, it’s often a sign something is off.
This isn’t just about how the interface looks or works. The tone, clarity, and responsiveness of the interaction all affect how users perceive the self-service experience.
Agent workload and reduce handovers
On the operational side, AI self-service should ease the burden on customer support teams by taking care of repeatable tasks. If agents are still answering the same basic questions day after day, the system might not be surfacing information clearly or at the right point in the user journey.
Tracking how often customers are able to resolve issues without being passed to an agent helps show whether the AI is doing its job and where it might need improvement.
Beyond self-service AI bots: Future trends
AI self-service is evolving in-line with broader developments in machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and enterprise automation. One area of focus is making the technology more adaptive—not just responding to inputs, but learning from previous interactions to improve how they guide users through a process.
There’s also growing momentum behind AI-powered communications that can carry conversations across channels without losing the thread. If someone starts a query in web chat and follows up by email or phone, they don’t need to repeat themselves or start over. Instead, the AI tool keeps track, preserving the flow of interaction.
Another likely development is tighter integration with back-end systems like customer relationship management (CRM) platforms and billing systems.
This will allow AI self-service tools to take more direct actions, like making real-time changes to a customer’s account or service subscription without bringing an agent into the loop. According to research by Gartner, by 2029, agentic AI will be capable of resolving 80% of common customer service issues without human intervention.
These changes are already starting to shape how organizations think about customer journeys, with self-service becoming a more central part of the support experience.
Empower your employees and your customers with AI self-service
AI self-service is becoming a core part of how organizations deliver faster, more efficient support. Done well, it gives customers more control over their interactions and takes day-to-day pressure off contact centers and support teams.
The real value, though, comes from how it’s set up. Success comes from building systems grounded in real user needs, designed around clear tasks, and supported by human oversight where it matters.
This creates space for agents to focus on higher-value work that benefits human judgement. Get this right, and AI self-service becomes a practical way to improve both the customer experience and how support teams work.
Dive into the full report, How AI is Changing Employee & Customer Experiences, to learn how top-performing companies are deploying AI to benefit their customers and employees.
AI self-service FAQs
How does AI self-service work?
AI self-service tools use natural language processing and machine learning to understand what the user is asking and guide them towards a resolution. This might involve answering questions, processing a request, or walking the user through a step-by-step process. These systems learn from past interactions to improve how they respond over time.
How is AI self-service different from traditional self-service options?
Traditional self-service relies on static menus or keyword-based searches, often requiring users to do more of the work themselves.
AI self-service tools can interpret natural language, ask follow-up questions, and take actions on behalf of the user, making the experience faster and more intuitive. They can also handle more variation in phrasing, and can typically follow through on tasks without needing agent involvement.
How do you measure the success of AI self-service?
A successful AI self-service system resolves requests smoothly, without needing to escalate. You might see fewer repeat requests, faster resolution times, and a noticeable drop in workload for frontline customer support teams.
When things aren’t working to plan, customers tend to abandon the process or ask to speak to someone directly. This can be a signal that it’s time to review and adjust the self-service experience.
Updated Feb 04, 2026