Since OpenAI unveiled ChatGPT back in late 2022, the world has been caught up in an AI whirlwind. As more organizations explore the adoption of AI, they’re looking beyond generative AI to machine learning (ML), predictive analytics, and other technologies.
As capabilities continue to evolve, the possibilities for AI seem endless. With so much money being spent on AI, it’s not just about quick gains. Most companies are interested in the expanding role of AI in the workplace.
McKinsey reports that 92% of organizations plan to increase their investment in AI technologies. So, let’s look at how AI usage in the workplace is transforming how we work today.
AI and automation in the workplace: Key takeaways
- AI is transforming modern workplaces through various technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing, generative AI, and robotic process automation.
- AI tools are being implemented across the business, from customer service and sales to operations and HR.
- The primary benefits of workplace AI include increased efficiency and productivity, improved employee satisfaction, enhanced customer experiences, and significant cost savings. AI also enables data-driven decision making, democratizes access to advanced analytics, and levels the playing field for businesses of all sizes.
- Challenges to AI adoption include job replacement fears and the risk of over-dependence on technology.
- Real-world applications include customer support automation, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, content creation, and virtual assistants.
- Companies like RingCentral are integrating AI to enhance internal collaboration and customer interactions.
- Organizations that embrace AI strategically while addressing its challenges will gain competitive advantages.
The technology behind AI tools in the workplace
AI is an umbrella term that encompasses various technologies capable of automating human tasks. These range from data entry to customer service, content generation, and beyond.
How these complicated technologies work is far beyond the scope of this article. However, it’s good to have a grasp on what machinery is driving the engine of the AI tools you employ.
Machine learning
Machine learning is a critical subset of modern AI tools that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time. Using ML, an application gathers feedback on its performance.
ML algorithms automatically parse data and learn from the results. However, for machine learning to be effective, it requires large amounts of data to make accurate predictions.
Deep learning
Deep learning goes beyond the performance evolution of machine learning. It takes the same approach but uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers. Essentially, it’s using several “brains” simultaneously to uncover complex relationships and insights.
These capabilities make deep learning more applicable for tasks such as image and speech recognition. In simple terms, ML follows specific rules while deep learning creates its own rules.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) enables devices to recognize and understand human language. It also drives AI chatbots or virtual agents to generate replies as text messages or audible speech.
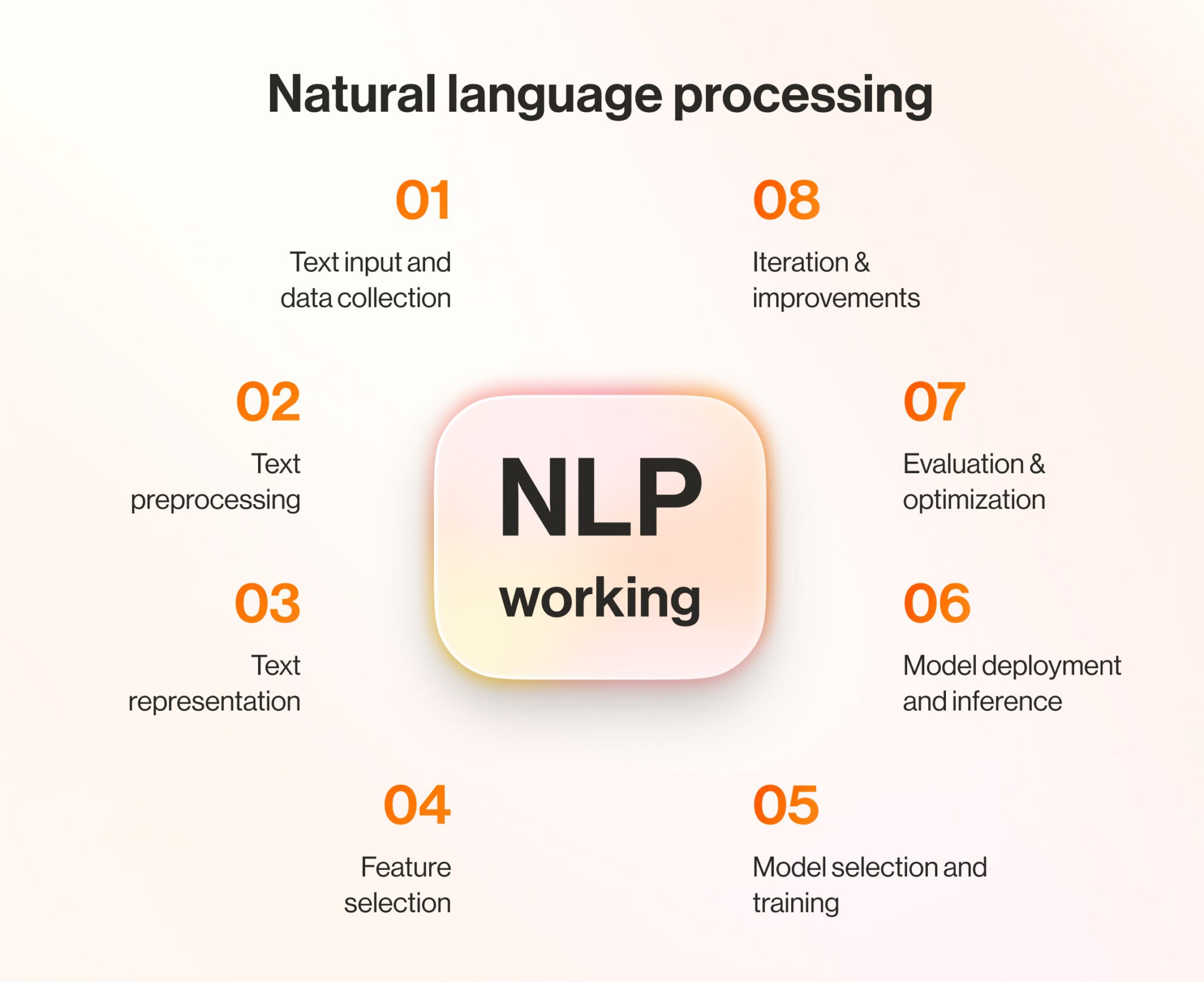
NLP combines with large language models (LLMs) to build a vocabulary of understanding. This provides insight and context during a conversation. For example, LLMs enable AI-powered business communications to create meeting notes or generate auto-replies.
Computer vision
Computer vision technologies are essentially the visual equivalent of NLP. This branch of AI enables machines to recognize and comprehend images and video. It powers AI that studies visual information and identifies patterns.
There’s a growing list of applications for computer vision, including combining it with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to visualize and assess robotics on an assembly line.
Generative AI
Generative AI, or simply GenAI, is a field that focuses on creating content such as text, images, music, and video. If you’ve used LLMs such as ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, you’re already familiar with these tools. Other examples include DALL-E 3 and Midjourney for image generation, Suno AI for music generation, and Runway for video generation.
Regardless of the content type, each generative AI tool must be trained on massive datasets to produce desired results. Using neural networks, NLP, deep learning, and other technologies, GenAI recognizes complex patterns. It learns from each piece of data, using it to inspire the generation of human-like content.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation uses software to take over repetitive tasks from humans. Software “robots” take over the burden of various administrative processes, such as data entry and form filling.
In general, software robots are coded with specific rules. They follow defined procedures to mimic human activities, such as logging into an application. RPA often integrates with ML, deep learning, and NLP to understand more complex tasks and manage unstructured data such as images and audio.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics is all about using data to peer into the future. Predictive modeling tools analyze historical data combined with real-time information. They use statistical algorithms to forecast future trends and outcomes. As the algorithms are constantly fed new data, they become more accurate over time.
Benefits of AI in the workplace
The capabilities of AI aren’t the only thing growing. A report from Precedence Research projects the AI market size to reach approximately $3.7 trillion by 2034:

The reason so many companies are embracing AI is thanks to the many benefits of automation and AI in the workplace:
Efficiency and productivity gains
One of the main benefits of AI usage in the workplace is that you get things done faster. Automated workflows take over repetitive and light tasks. They enable your team to focus on strategic activities.
Of course, it’s not only about speed. RPA and other AI-powered technologies are more consistent and reduce human error. That means you get more accurate results in less time.
Improved employee engagement and satisfaction
AI can improve the quality of life for your employees. Automation takes over the more menial tasks that frustrate and often bore your team. At the same time, tools like predictive analytics and virtual assistants help people perform at a higher level. For example, an AI-powered assistant might automatically organize and filter email.
Another way to keep employees engaged is to offer true growth opportunities. AI learning platforms can personalize professional development, helping employees build skills that align with their career goals and interests.
When employees spend less time on busy work and more time on meaningful work, job satisfaction increases.
Better customer experiences
Today’s customers expect personalized, immediate service. With the help of AI in customer service, you can meet both expectations. NLP-powered chatbots provide an easy way for any company to offer 24/7 customer support. They can also deflect lower-level problems and escalate and route customer calls when necessary.
AI tools integrate data from website analytics, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and other sources. This enables them to personalize interactions and craft messaging that resonates with different audiences.
Easier data-driven decision making
AI presents a solution to collecting, managing, and analyzing vast amounts of information. AI-driven tools can streamline data management and democratize data analysis. You don’t have to be a data scientist to mine insights. You only need to know how to generate reports.
AI-powered analytics tools identify trends, spot anomalies, and surface opportunities in your data. They present findings in clear, visual formats that make complex information easy to understand. You can respond and act quickly to market shifts or operational issues.
Greater access to innovation
AI has lowered barriers to entry for innovation by putting advanced capabilities within reach of businesses of all sizes. Cloud-based AI services mean you don’t need a massive IT budget. You also don’t need a team of specialists to leverage cutting-edge technology.
Scalable AI services level the playing field. They accelerate innovation cycles across entire industries. You can rapidly experiment with new ideas and iterate on solutions regardless of size or technical resources.
Cost-savings
It’s no secret that AI requires an upfront investment. Some deployments range in the tens to hundreds of thousands of dollars. However, the long-term cost benefits can be substantial.
An obvious opportunity is with RPA and automated workflows. Automation reduces labor costs for routine tasks while improving accuracy and reducing the cost of errors. By using generative AI in the workplace, meanwhile, you can streamline content creation, reducing the wages spent on creating marketing materials.
AI monitoring systems can identify potential issues before they become costly problems. These include monitoring operations, security, and compliance. Artificial intelligence tools optimize resource allocation and minimize waste. You only spend what you need.
Return on investment (ROI)
AI drives efficiency by optimizing resources and helping your team work smarter. Employees are happier, focusing on more complex and strategic tasks. When used effectively, AI tools boost productivity and worker output.
Using AI in sales helps employees focus more time on targeting, tailoring interactions, and increasing revenue. When combined with the cost savings, the returns can be substantial.
For example, Snowflake reports that an investment in generative AI delivers an average ROI of 41%.

Empower remote working
More than 21% of US employees work remotely. Virtual assistants empower long-distance team members to perform their jobs efficiently and stay connected with the organization. They’re available around the clock to help with repetitive tasks. Gen AI tools provide feedback and streamline content creation when no other team members are available.
AI can also help schedule meetings and optimize schedules for remote team members working across various time zones. This ensures everyone is available for important discussions.
Potential disadvantages of AI in the workplace
There are pros and cons of AI in the workplace. We’ve listed the advantages, so it’s only fair to go over some of the potential disadvantages.
Ethical and privacy issues
More data is being generated and collected every day. It’s no wonder that consumers are growing concerned, with 1.35 billion individuals compromised by security breaches in the US in 2024. People aren’t only worried about data protection but also about how companies are using their data. The same goes for your employees.
You can alleviate fears about ethics and privacy by putting a strong data governance framework in place. Create data management policies and procedures that promote transparency, traceability, and privacy. Train employees on ethical, secure data handling and protecting sensitive information.
Regularly audit your AI analysis reports to identify and eliminate any biases that can creep up in neural networks and algorithms.
Fear of job replacement
While AI delivers many benefits, we can’t ignore the fact that it is taking over more routine tasks from humans every day. Fear of job replacement is a legitimate concern for workers.
A Forbes Advisor survey reports that 77% of employees are at least somewhat concerned about losing their jobs to AI:
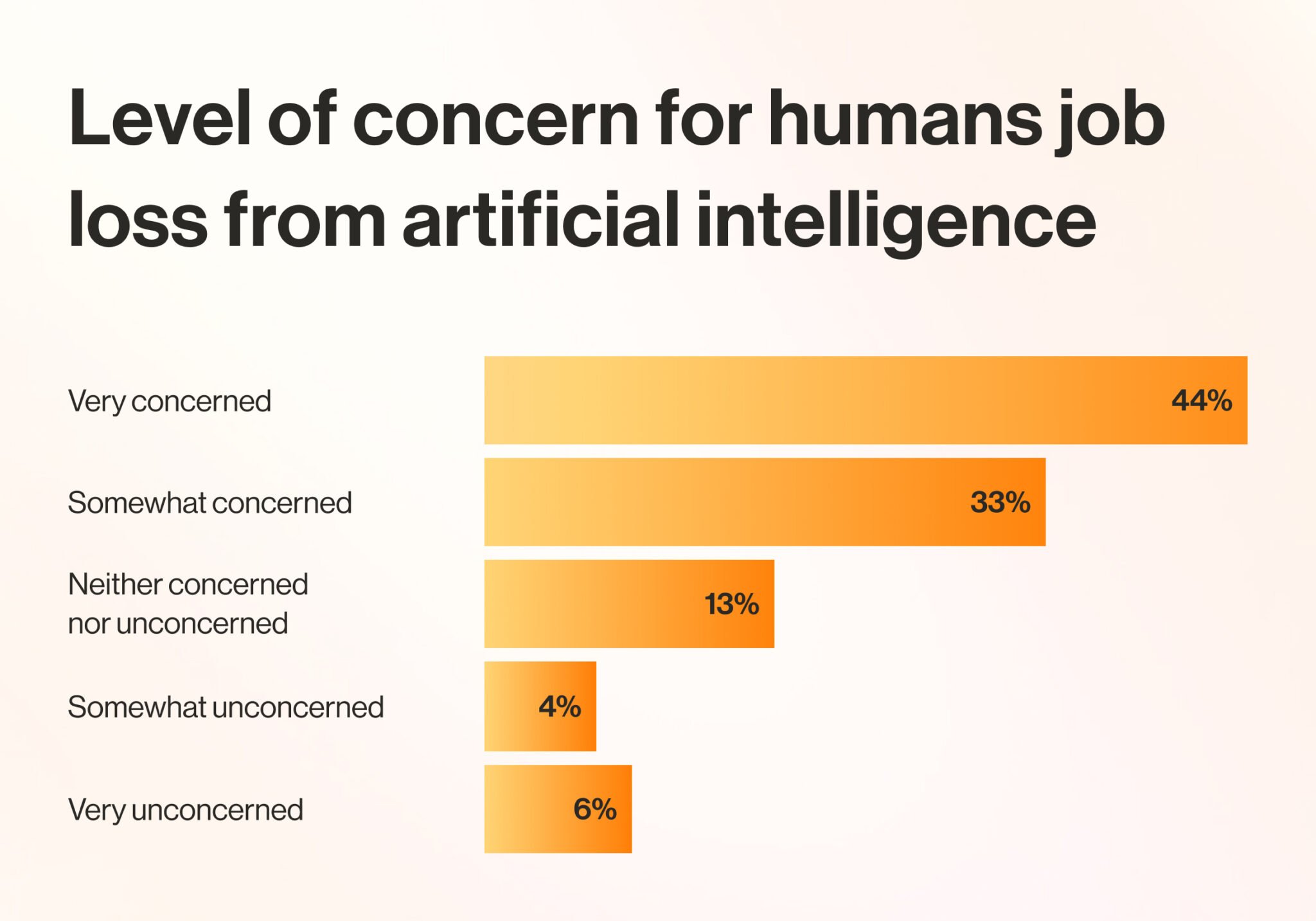
While it’s true that some jobs will be eliminated or reduced by AI tools, new ones will also be created. Roles will evolve and materialize that require humans to manage and monitor AI usage in the workplace.
The key to addressing job replacement concerns is change management and open communication. Focus on helping employees understand how their roles will evolve and what new opportunities AI creates. Ironically, AI-powered HR tools can help identify these emerging opportunities.
Always be transparent about your AI implementation plans. Involve employees in the process with webinars, meetings, and team messaging channels. Emphasize that the goal of AI usage is to eliminate mundane tasks and improve performance, not necessarily to replace jobs.
Reduction in human interaction
While AI excels in certain areas, it still lacks a human touch. For example, the best LLMs and other tools lack the emotional intelligence and empathy of your team members.
These deficiencies become particularly glaring during customer service and support interactions. Conversational AI provides human-like interactions, however, customers often become frustrated dealing with virtual agents. Five9 reports that 75% of people still prefer talking with a human agent for customer support.
The solution isn’t to avoid AI, but to use it strategically. Deploy AI for initial customer interactions and routine inquiries. However, ensure it’s easy for people to reach a live team member if desired or when needed. Maintain human oversight of AI decisions with monitoring, audits, and customer feedback surveys.
Skills gaps and overdependence on technology
Other potential drawbacks of AI usage are skill erosion, lack of personal development, and eventual overdependence on technology.
Recent research from MIT suggests that ChatGPT users recorded lower brain activity and cognitive function across neural, linguistic, and behavioral levels. Additionally, 83% of LLM users had difficulty quoting their own essays.
That’s only one study with a small sample size. At the same time, it’s logical that overuse of AI can lead to a lack of skills with your team.
To combat this, educate employees on suitable usage of AI that maintains their input and touch. Additionally, address skill gaps with training partnerships and learning development systems (LMS). These empower your team to take assessments and skill up in areas that are relevant to their role and career goals.
Examples of AI in the workplace
As AI evolves and new technologies emerge, the possibilities are nearly endless. However, you’re not looking to weigh your future on the unknown. You want to implement artificial intelligence to deliver results now.
Let’s take a look at some AI in the workplace examples:
Customer experience and support
There are many use cases for AI to boost customer experience and support. Platforms like RingCentral provide many capabilities to guide your agents and empower your customers.
Enhanced customer support
AI technologies transform the customer support experience through intelligent automation. For example, AI built into RingCentral’s communications solutions can automatically transcribe every conversation and sync call summaries directly with your CRM and ticketing systems.
Post-call work, like updating customer records and creating follow-up tasks, can be reduced by up to 20% through AI automation. This means shorter wait times for customers and more productive agents.
Virtual agents and chatbots
Speaking of customer service and support, some platforms are powered by conversational AI. This artificial intelligence goes beyond transcribing and handling repetitive tasks. It powers virtual agents who act as first-line service and support for your customers, available every hour of the day.
Sentiment analysis and AI assist
AI calling tools often include real-time sentiment analysis that improves customer interactions by informing agents and reps of the emotional state of the customer.
For example, RingCentral RingCX provides your agents with deep customer insights during a conversation. The AI helps them empathize and understand. It also guides agents to find solutions and de-escalate potentially explosive situations. Live AI coaching increases first contact resolution (FCR) by 35%.
Sales and marketing
AI can streamline sales and marketing funnels, guiding your team to the right prospects.
Sales outreach and qualification
AI sales tools can enhance activities like outreach and lead generation. Smart sales dialers prioritize prospects based on demographic and behavioral data. They also eliminate time between calls so sales development representatives (SDRs) are more productive.
You may also use AI to analyze prospect behavior across multiple touchpoints, including email opens, website visits, and social media engagement. AI qualification tools can then score leads on the likelihood to purchase. That helps the sales team focus on the prospects most likely to convert, resulting in more qualified meetings and shorter sales cycles.
Content creation
With the rising popularity of generative AI in the workplace, content creation might seem an obvious application. It’s not just for help with writing blogs or content marketing, though.
You can also use GenAI tools to help with writing website copy and social media captions, or to produce hero images, videos, and royalty-free music to accompany your marketing campaigns.
Sales forecasting
Many industries use predictive analytics to improve the accuracy of their sales forecasts. One example would be a multinational retailer analyzing its historical data to predict revenue. These metrics can be living, breathing targets that update in real-time as more sales data comes in. Neural networks and algorithms become more accurate with future predictions.
Legal admin, risk management, and compliance
AI is also streamlining many time-consuming legal and compliance tasks across industries.
Legal process automation
Making deals and forming partnerships is time-consuming. Delays lose momentum. Document intelligence platforms can summarize legal agreements and flag potential issues. AI legal tools can also create approval workflows based on contract value and risk level.
Risk management and compliance
AI can also helps identify potential compliance violations or risks before they escalate. ML tools can monitor communication channels for language that may indicate misconduct or fraud. They can also flag patterns in transactions or behaviors that deviate from established norms.
For example, a financial institution may use AI risk management tools for internal auditing of transactions, looking for misconduct or illicit activities.
Operations and infrastructure
AI technologies help you optimize your operations for cost savings and better decision-making.
Predictive maintenance
AI uses data from IoT sensors and historical records to forecast equipment failures before they happen.
For instance, a food processing facility may use AI to monitor critical equipment like conveyor belts, refrigeration systems, and packaging machines. By analyzing performance data, the system predicts when components will fail and schedules maintenance during planned downtime. Managers can now plan shift patterns around maintenance and plan for alternative activities.
Supply chain and inventory management
AI is also being used by organizations to analyze large volumes of data and monitor global supply chains.
Predictive algorithms take into account weather, geopolitics, and other historical data. They analyze information and alert you to possible disruptions. What that means is that you maintain stock levels to meet customer demand and gain a leg up on the unprepared competition.
Energy optimization
AI drives smart energy systems that optimize resource allocation. Systems can connect to IoT devices to adjust heating, cooling, and lighting depending on whether rooms are in use or not.
This can prove especially useful for businesses with lots of hybrid and remote employees, where office staff numbers can change daily.
In a different example, a restaurant group may use AI to adjust temperature settings in real-time depending on ambient weather conditions and the number of customers.
Workplace productivity
One of the greatest effects of AI in the workplace is increased productivity. Here are some examples of how it can work:
Virtual assistants
AI-powered virtual assistants provide remote and on-site team members with digital secretaries.
Think of AI tools like Siri or the Google Assistant. The difference is that these virtual assistants can be highly specialized and integrated with specific platforms. For instance, a doctor can use an AI assistant to draft or refine patient notes and educational materials to save time.
Appointment scheduling and space utilization
Setting up meetings is increasingly difficult for companies with remote employees in different time zones.
AI can monitor when team members are working or have presence and identify patterns. It then schedules appointments with customers or team members at optimal times. This includes the booking of meeting rooms in shared or private offices.
Collaboration and communication
AI empowers internal collaboration and communication for businesses. For example, RingCentral RingEX uses AI to capture meeting notes in real-time, including key updates and action items. This enables every attendee to be more present in meetings and actively participate. Meeting summaries can also be sent to those unable to attend to keep them informed of the important details.
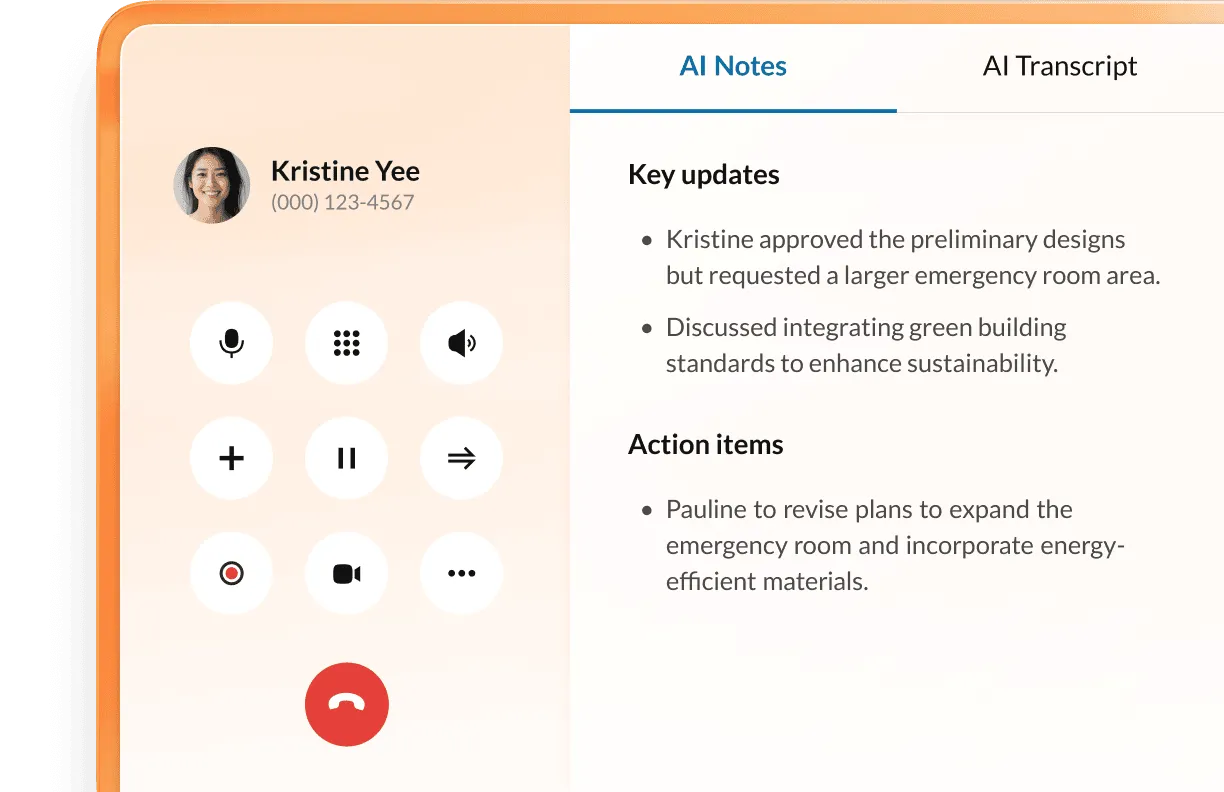
Another feature of AI-powered communication platforms is accurate translations. Team members working in different parts of the world who speak different languages can easily connect.
Ready to start using AI in the workplace?
Investing in AI platforms and solutions can bring immediate and long-term benefits for your business—it doesn’t matter if you’re a start-up or an enterprise.
What AI is capable of doing is only likely to progress and become more advanced, too. Adopting intelligent solutions now helps you stay ahead of the curve. Use AI to increase productivity, promote collaboration, enhance the customer experience, optimize your resources, and more.
For those who want an AI communication platform that takes internal and external communication to the next level, RingCentral is here to help. Our business communications solutions will have your team working together efficiently regardless of location or language.
Get in touch today and find out how RingCentral can bring AI to your workplace.
AI in the workplace FAQs
How is AI being used in the workplace?
AI is being used across multiple workplace functions. These include customer service, sales and marketing, operations, and productivity. Common applications include automating repetitive tasks and enhancing communication and collaboration.
How does AI increase efficiency in the workplace?
AI increases workplace efficiency by automating routine tasks. It reduces manual errors and accelerates decision-making. AI tools can handle data entry, schedule meetings, generate reports, and process large volumes of information in seconds.
AI also enables predictive analytics that help businesses anticipate problems and opportunities. Virtual assistants and chatbots free up employees to focus on higher-value strategic work.
Is AI a threat to the workforce?
AI is not necessarily a threat to the workforce. Rather, it’s a tool that changes how work is done. While AI may eliminate some routine tasks, it also creates new job opportunities in AI management and data analysis. Most successful AI implementations focus on enhancing human capabilities rather than replacing workers.
Updated Feb 04, 2026