The world is always changing. Information technology continues to evolve at an ever increasing pace. Large organizations need a framework to understand new technology and how it relates to business strategy.
Whether it’s cloud computing, machine learning, or automated analytics, businesses need a plan that decides what innovations to invest in and how to use them.

Enterprise architecture (EA) is the way by which businesses plan to adopt and utilize technology to meet their desired business vision.
But within that plan, there must be pathways to allow for flexibility and guidance. Communication, analysis, and feedback must be constant to adjust to the inner workings of the bigger picture of the business. This can be facilitated by tools like video call platforms or a virtual phone service to ensure continuous and effective communication.
What is enterprise architecture?

Enterprise architecture is the methodology by which an organization plans and arranges IT infrastructure. The components of EA are analysis, design, planning, and implementation. Architectural framework principles guide the organization through business, information, process, and technology strategies, all with an eye to reaching the desired business outcomes. For example, a virtual call center can be part of your EA to improve customer service and operational efficiency.
Enterprise architecture was first conceptualized in the 1960s under the term of Business Systems Planning (BSP). But the widespread implementation of enterprise architecture frameworks was a result of rapidly increasing business technologies in the 1980s. EA had become a means for combining legacy applications with current and future processes, a concurrent implementation allowing an organization to optimize business capabilities.
Today, EA has further developed to encompass various other methodologies. These range from quite general to industry-specific architecture frameworks. Some models emphasize different domains or goals depending on management resources and business vision and outcomes. For instance, a tech company from Silicon Valley will aim to increase shareholder value. Whereas, a government agency will aim to improve the end-user experience.
Why is EA important?
The business world is changing more rapidly than ever. New technology such as virtual calling, conference call services, and workforce management tools are changing the way people work, allowing team members to collaborate from anywhere at any time. Enterprise architecture describes movable pathways for achieving business goals against a time horizon. All whilst staying flexible to adopt new tools and technologies when beneficial. As tech evolves, EA helps to keep a balance between IT performance and business development.
What are the goals of enterprise architecture?
The purpose of EA is to form a cohesive and comprehensive blueprint of how an organization is structured. An enterprise architecture model paints a big picture of the entire organization, with a long-term view. This blueprint describes the business processes, hierarchical structure, information systems, and technologies. It also allows room for the adoption of modern innovations.
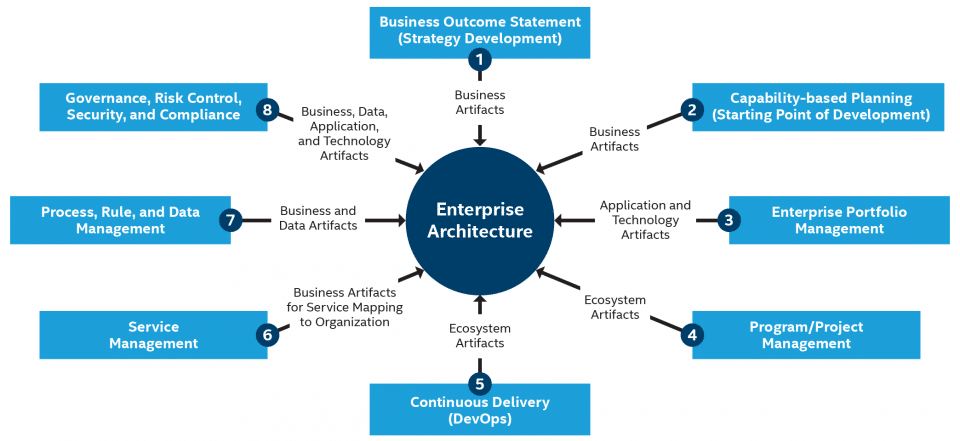
But EA is also a roadmap to guide an organization with planning and maintaining business goals over time and bolstering them through technology. General goals of any EA are:
- Effectiveness. EA establishes a workflow for essential and accurate processes. An EA blueprint defines how to reach deliverables set out by the business.
- Efficiency. The ability to reuse resources and eliminate redundancies is clearly set out within the framework. Business process modeling and workflow mapping can produce greater collaboration.
- Agility. Organizations look to EA to make sense of combining legacy technology and new technology adoption. A correct model will assess technology risks, as well as guide the monitoring, metrics, and analysis needed to identify when and how to evolve IT in alignment with business goals.
- Continuity. Nothing is more important to leading enterprises than being able to maintain mission-critical business operations. EA allows for the highest level of continuity through standardization of business and IT processes.
While an EA framework can guide and improve many aspects of an organization, the ultimate purpose of EA is to maximize value. It is up to the enterprise to define that value.
What are the benefits of enterprise architecture?
In today’s world, technology like multi-cloud and AI automation has caused IT systems to become extremely complicated. A well-structured EA promotes a comprehensive understanding of the entire business.
Additionally, EA lays out the blueprint for future improvement of infrastructure and digital transformation of the business.

Design
Enterprise architecture provides support for the structure of the entire organization. This design lays the groundwork for flexible planning to reach business goals. It also helps with organizational redesign such as during mergers, acquisitions, or other organizational change.
Standards
Organizations look to EA to enforce discipline and standardization of business processes. It also enables process consolidation to improve efficiency. Or it can eliminate redundancies created by new technology advancements, as well as promote asset reuse and integration.
Project management
Organizations will find EA supports work prioritization for project portfolio management. It also supports rapid investment decision making through data modeling. On each individual project, EA enhances collaboration and communication between stakeholders. Deliverables are more defined, in line with the overarching business vision, and consistent for each team.
Discovery
Enterprise architecture sets out at a consistent and repeatable path for architecture documentation. This not only increases accountability but can quicken the discovery of IT or business requirements. Faster discovery means organizations will be faster to find a solution.
System development and management
Optimal system designs provide an efficient allocation of resources. EA practices make testing and development consistent and timely. With EA enforcement of standardized IT practices, teams can produce quicker decisions when it comes to adopting new technologies.
IT complexity and value
EA minimizes redundancies across the IT infrastructure. It reduces the systems implementation and operational costs. The reduction of IT complexity directs consolidation of data and applications. Less complex IT function allows for better interoperability of the systems throughout the IT infrastructure.
IT openness
Organizations using EA will have a more open and responsive IT system in place. This is because EA paths increase accessibility and availability of data, which is availability that simplifies regulatory compliance. EA also increases transparency for the entire organization, promoting collaboration.
IT risk management
Business risks from security or system failures are reduced by implementing an EA blueprint. Better standardization and communication ensure more scrutiny and quicker problem-solving. Therefore, EA also supports the organization in maintaining consistent and reliable deliverability.
What are the six basic elements of enterprise architecture?
There are many components that make up the EA model. Enterprise IT infrastructure varies, and business needs are organization dependent. But all EA framework consists of the same core elements.
1. Architecture management
Each enterprise will need an oversight team for the architecture. They make sure everyone else stays on track. The team is there to ensure alignment of business goals with IT infrastructure.
2. Architecture framework
This is the model or methodology that defines the architecture. It is the blueprint that defines the big picture for enterprise strategy, including the required IT infrastructure.
3. Implementation methodology
These are the steps required to implement the strategy laid out by the framework. Implementation directs a project all the way to completion.
4. Documentation artifacts
This is where the organization documents strategy, plan, and workflow. IT solutions must be set up to fit the needs set out by the framework and implementation. Your documentation artifacts record all changes and processes, and must be kept up to date.
5. Architecture repository
This is the enterprise toolbox. All of the resources and processes that an organization has will be available. Teams can use any tools as they deem necessary to accomplish the goals set out by the framework.
6. Associated best practices
Best practices are where the organization creates standardization of their operating procedures. This enforces consistency of processes and compliance. But it also promotes transparency, so teams understand the deliverables (documentation artifacts).
The 4 domains of enterprise architecture
EA defines organizational structures, layer upon layer. Four layers combine to form the entire architecture.
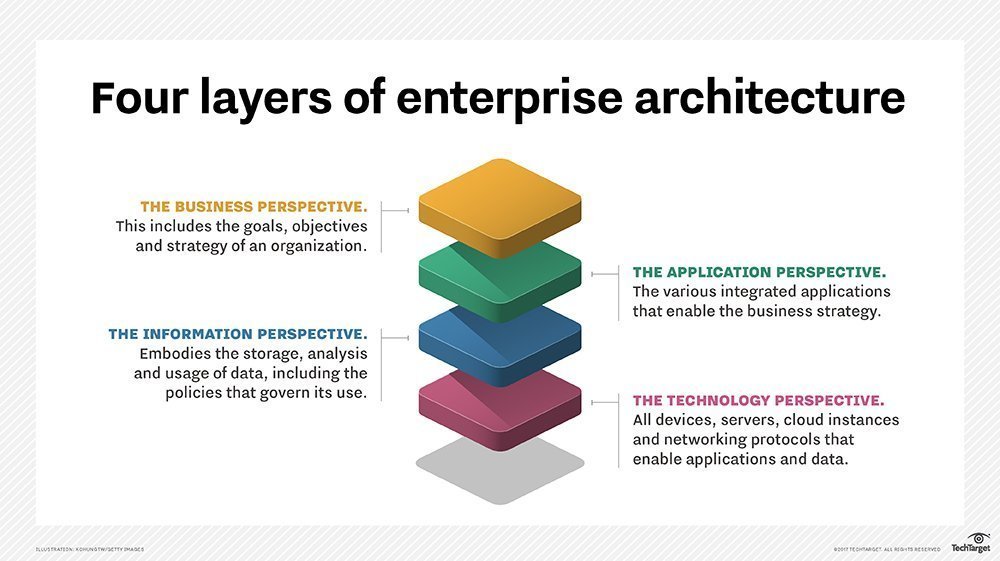
1. Business
EA arranges daily business processes, such as organizational structure and business relationships. It also includes the business functions, goals, and overall strategies of the organization.
2. Applications
Application architecture identifies the applications, their interactions, and relationships to the core business. It describes how business capabilities or services are implemented.
3. Information and data
Data architecture concerns data center structure and the management of data resources. Data analytics improve other aspects of the infrastructure in a positive feedback loop. This allows for the most effective IT performance and optimal flexibility of business processes.
4. Technology
The software and hardware needed to implement the other domains are laid out by the technology architecture. In turn, the business processes evolve concurrently with IT.
What is an enterprise architecture pattern?
EA models vary in design according to need. An architectural pattern is a solution to a commonly occurring problem.
In software architecture, EA addresses issues within engineering, hardware limitations, availability, and risk. For example, when managing a contact center, an EA pattern might guide the integration of systems to ensure reliability and efficiency. An enterprise architecture pattern is not the architecture itself, but a design element. These patterns are specifically suited to their particular domain. However, these patterns can be easily repeated in other areas aiming to achieve the same benefits.

Methodologies
This enterprise architecture description can seem general and quite vague. But there are many different frameworks for implementing enterprise architectures. There is not one general framework that fits every business model. Every organization requires different components and systems to reach its goals—some may want security architecture, others information architecture.
Three examples of enterprise architecture planning (EAP) methodologies
The Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework (FEAF) is a reference model to guide federal agencies. FEAF provides a common approach for diverse agencies to work together on strategy and management. Several benefits include resource sharing and reduced costs. The stakeholder in this model is each individual citizen. And the ultimate goal of FEAF is to improve the overall experience of the stakeholder.
The Zachman Framework for Enterprise Architecture is a fundamental structure that involves a 6×6 framework. It is a template used to organize and analyze data, but can also be used as a framework for EA.The framework provides a logical structure for classifying and managing complex items within 36 descriptive boxes.The aim of the Zachman Framework is to give different perspectives. It allows different stakeholders to look at the same thing from different points of view.
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) outlines directives for design, implementation, and governing of enterprise IT architecture. TOGAF focuses on flexibility through standardization and modular design. It was created to manage the life cycles of pre-existing components such as legacy applications. This makes new technology adoption much easier for large enterprises by allowing them to include legacy infrastructure in EA design.
Other EA methodologies may provide strategy and management for specific types of enterprises. For example, the Ministry of Defence Architecture Framework (MODAF) is designed with the military community as the primary stakeholder.
What is an enterprise architect role?
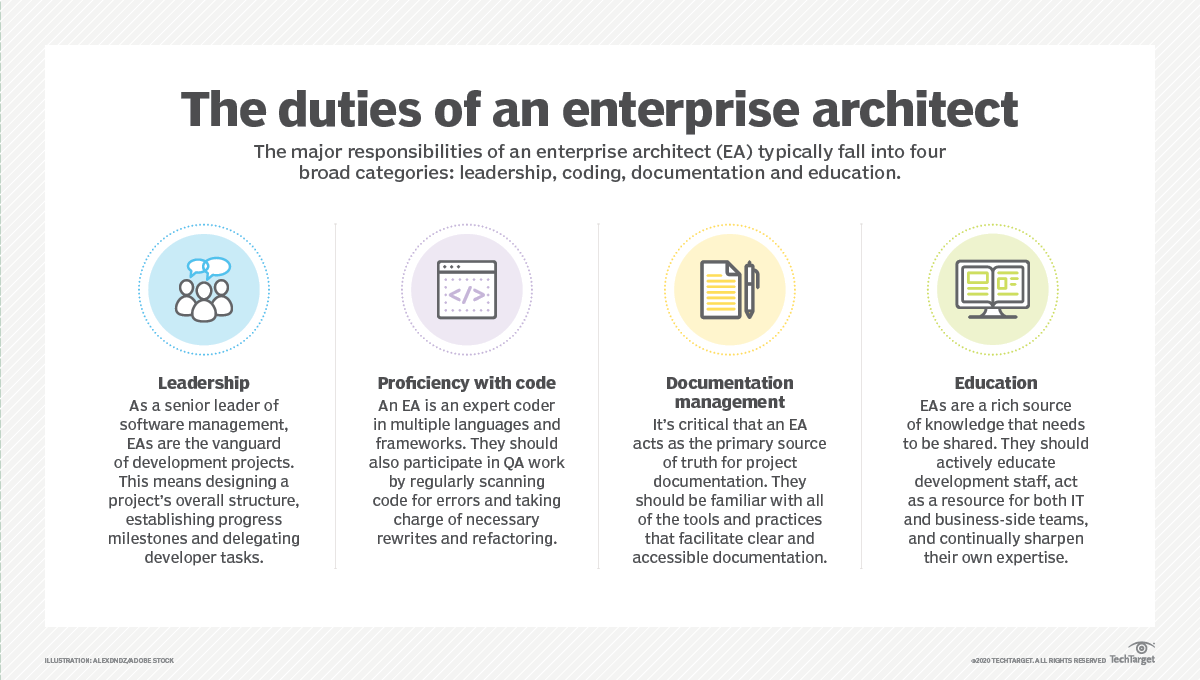
An enterprise architect guides IT implementation to reach business goals. This means enterprise architects need to be able to talk to both technical developers and business managers. It is an enormous responsibility, requiring a lot of identifying and analyzing as well as more hands-on work. Architects work directly beneath the chief technical officer (CTO) or chief information officer (CIO).
The enterprise architect must stay on the cutting edge of technology trends. They need to have the systems in place for deciding which new tech aligns with the company’s framework architecture.
This role is typically for someone with a degree in computer science and 10 plus years of IT experience. Enterprise architects are familiar with a vast amount of computer system technologies. But also have management skills like communication, teamwork, and leadership.
Desired certifications
The enterprise architect role is highly specialized. But it also requires general knowledge of hardware and software alike, as well as IT experience. On top of experience, enterprise architect hopefuls will need to demonstrate their IT competence. Candidates for the enterprise architect role will need one or more of the following certifications:
- AWS Certified Solution Architect
- Axelos ITIL Master certification
- Dell EMC Proven Professional Cloud Architect Training and Certification
- Google Professional Cloud Architect
- Professional Cloud Solutions Architect Certification
- Red Hat Certified Architect
- Salesforce Certified Technical Architect (CTA)
- The Open Group TOGAF 9 Certification
- The Open Group Certified Architect (Open CA)
This is not an exhaustive list. There are many more certifications available, tailored to enterprises in specific industries.
Plan for the future
Enterprise architecture will guide your organization through the turbulent times ahead. Maximize the value of your organization. Stay agile with technology adoption of cloud computing, AI, machine learning, and whatever future state may come.
Choose a framework that fits your enterprise and gain the benefits of flexibility. An EA framework will optimize the structure and processes of your organization. But in the end, using EA to guide your organization will maximize stakeholder value and help you change toward your desired business goals.
Originally published Jan 12, 2021, updated Sep 12, 2024





