What is Return On Sales (ROS)?

Return on sales is a vital metric in any business operation to ensure it’s running efficiently and working toward your bottom line. Having adequate return on sales (ROS) ensures that your company has sufficient cash flow, taking into consideration things like business costs and all channels of income.
Return on Sales—also known as ROS, Operating Margin, or Operating Profit Margin—is a standardised financial ratio that describes profitability as a percentage of sales revenue. This ratio helps businesses assess how efficiently a company can convert revenue to operating profit. It considers the basic efficiency of your business by converting investment into profit while factoring in things like amortisation.
The Importance of ROS
The importance of ROS cannot be overstated. It allows you to monitor the overall performance of your business and helps you get a high return on your investment. Different companies will have different processes that factor into their return on sales.
However, ROS benefits businesses in much the same way if it is tracked consistently over time. Here are some reasons that ROS is an important metric in your company.
Measures Success
The single percentage produced by the ROS becomes a baseline metric that you can use to measure your business’s performance over time. It allows you to perform a simple trend analysis that gives an accurate picture of reinvestment potential and the ability to pay back loans and dividends.
An increasing ROS illustrates that the company is growing efficiently. Alternatively, a decreasing ROS may signal imminent financial troubles. The power of this metric is best seen over time because it is most useful to track progress and setbacks, compared to the lack of context provided by an isolated number.
Monitors Production Efficiency
Using ROS also allows you to check how effectively your business is producing its core products and services. It can indicate efficiency and profitability. If you have a low or decreased ROS, consider whether the problem lies in production. You can then decide to change suppliers, increase prices, or integrate new technology to increase your overall profitability ratio.
Informs Stakeholders and Decision Makers
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to your business. Calculating your ROS allows you to go to your stakeholders with data on how your company is doing. It will give them the information they need to assess your reinvestment potential. It can also help management make decisions that will optimise your business processes.
How to Calculate Return on Sales

Calculate/Locate Net Profit

When calculating ROS, you may notice that some companies report revenue while others report net sales. To determine net profit, you take total revenue minus the credits or refunds paid to customers for returns. Net profit or operating profit is most often used in the retail industry.
You can also find this information on your income statement. Be sure that you don’t include non-operating activities and expenses, like income taxes and interest expenses. This is the reason the net profit in ROS is also called EBIT or earnings before interest and taxes.
Input Numbers into Equation

The equation takes the net profit and divides it by net sales, also called net revenue. The expanded equation is ((Sales Revenue)-(Operating Expenses))/(Net Sales)=ROS.
Example of Return on Sales Formula
Now that we have a formula, we can work through an example to see how this would function within your business. In this example, a clothing company using an ecommerce platform is trying to calculate their ROS to determine their operational efficiency. They have gathered all their financial statements which detail their operating expenses and operating income.
Here is the data:
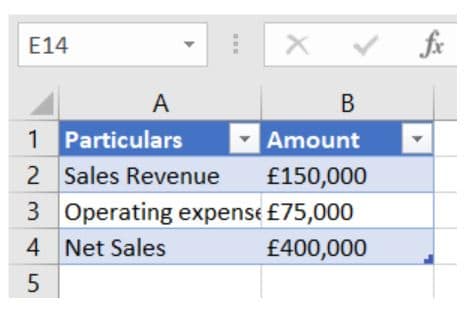
Now, you subtract operating expenses from sales revenue.
£150,000 – £75,000 = £75,000 = Net Profit
f you are starting with net income, you can calculate the EBIT using net income, interest expense, and taxes paid. The formula is: EBIT = Net Income + Interest + Taxes.
£65,000 + £6,000 + £4,000 = £75,000 = EBIT
You can modify EBIT to include depreciation and amortisation, as well. You just need to add depreciation and amortisation to the net income, interest, and taxes to calculate the EBITDA.
Finally, you can use the EBIT or the net profit to figure out your ROS.
£75,000 / £400,000 = .1875 = 18.75%
So, your ROS is:
18.75%.
Resources
How to Use ROS
Return on sales is used by various stakeholders to estimate how well a company can leverage its operating efficiency to increase its net profit margin from net sales. This comparison helps analyse trends and internal efficiency over time. ROS is used to understand whether turnover is converted to gross profit.
Return on Sales Formula Calculators Online
Here are some of the options you have for quickly calculating your ROS:
Return on Sales FAQs
What is a good return on sales?
For most companies, a ROS between 5% and 10% is excellent. This may not seem like much, however, if your business is heading into financial trouble, this number would be in the negative. If ROS is above 0%, you are turning a profit. You are working to improve your efficiency ratio, but there is a limit to how much you can reduce cost or raise prices.
Is a higher return on sales better?
Yes. A higher ROS means that your company is managing its operating costs and revenue channels well. A better indication for growth is looking at the trends over time. An increasing ROS shows the company is growing productively.
How do I calculate net sales?
To calculate net sales, you subtract gross sales by the number of discounts, sales, returns, and allowances that occur over a specific timeframe.

Takeaway
Return on Sales is an important indicator of how your business is doing. If you complete the calculations and are not where you want to be, consider where your business can reduce cost or find ways to raise prices without compromising customer satisfaction.
One way you may be able to consolidate is in your VoIP provider. RingCentral can be your one-stop-shop for a better customer experience that helps you bolster your bottom line.
Originally published Jul 19, 2021

