Cloud computing technology is evolving at an ever-increasing rate. Organisations are moving to cloud services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) for agility and flexibility in uncertain times. But cloud computing solutions can also increase efficiency and raise productivity. In other words, enterprises using cloud technology will be able to increase value for the end-user.
Cloud computing services aid businesses in making a digital transformation. Mobile cloud computing provides an effective solution for the virtualisation of unlimited resources. It can supply high performing applications to a broad segment of users.
Mobile Cloud Computing
Mobile cloud computing (MCC) uses cloud architecture to provide services to users on their mobile devices. This means that data and processing occur not on the mobile device itself but on cloud-based resources. The user interacts with the cloud via a mobile application such as a social media app.
The purpose of MCC is to provide flexible and available resources that are accessible online. Cloud resources include storage, processing, and functionality over the internet via mobile networks.
Mobile cloud services like Microsoft Azure support the execution of rich mobile applications. These apps must be accessible from a broad range of devices including those with old technology and inferior hardware. Performance must be consistent across all devices and networks. Subscribers will expect the same rich experience they would get from desktop applications.
Characteristics of a Mobile Cloud
For MCC to be effective and accomplish its purpose, it must have several key elements.
Firstly, like all cloud computing technology, MCC infrastructure is based in a cloud environment.
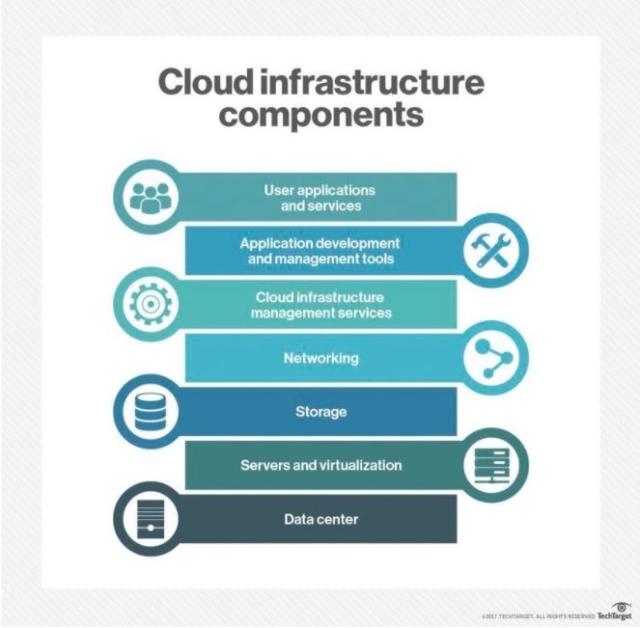
A Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud Backbone
The backbone of the cloud is its physical servers in cloud provider data centers. These are maintained and upgraded by the provider. The backbone is responsible for allocating the hardware resources.
Supervisor Software
Cloud supervisor software comes in many packages. The OS installed on the servers automates the resource allocation. For IaaS, a hypervisor allows and manages user-created virtual machines (VMs). For PaaS, the hypervisor contains and manages the provider’s software stack. Middleware manages the interaction between jobs running concurrently on the cloud.
Software Infrastructure
This is where the allocation of network resources is managed for platforms and services provided to the end-user. Essentially, this is where cloud management of IT services is available.
Platform Infrastructure
PaaS is provided by a cloud vendor for web application development. The cloud infrastructure allows for the virtualisation of computational machines. This is where APIs like Google App Engine and Apex Cloud are hosted and available for users.
Application Layer
This is the fully fleshed out interface that the user encounters. User application data is stored on servers in the provider data center.
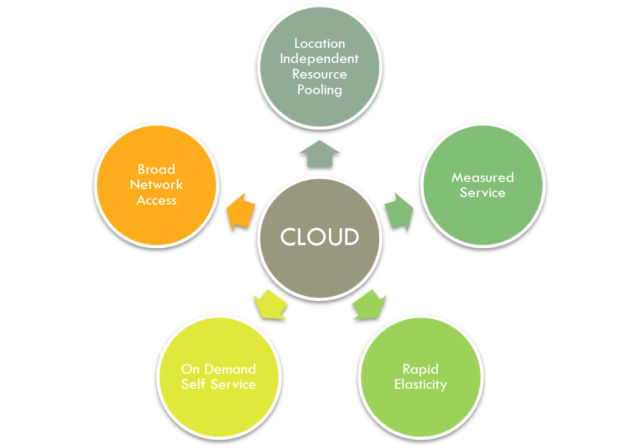
In general, cloud computing features:
-
- Resource pooling
- On-demand self-service
- Provider maintenance and oversight
- Scalability and rapid elasticity
- Availability
- Automation
- Cost-effectiveness
- Provider monitoring and security
- Transparent pricing with pay as you go
- Measure service and monitoring tools
Users of MCC can expect those same elements when using cloud applications and services. However, this is combined with mobile computing technology to provide
Data Cache
Resources are available on the cloud, but performance depends on mobile connectivity. Some information is accessible at all times, regardless of a connection to the internet. With MCC, the solution is to maintain a data cache locally on the device. This also increases the performance and security of sensitive data.
User Accommodation
Mobile user requirements can vary widely in scope depending on device OS and operating specs. MCC applications must be able to meet these requirements to maintain user availability.
Easy Access
Mobile applications must be simple and streamlined. The user experience on a mobile device should be equal to that of the desktop app. Moreover, performance must stay consistent or the mobile app loses its purpose.
Cloud Apps
MCC facilitates cloud access to new services that are not available to non-mobile users. It does this through cloud apps available in Apple and Google stores as well as native cloud-based APIs.
Benefits of a Mobile Cloud
MCC combines mobile computing with cloud computing technology. This combination provides the many improvements gained from using cloud architecture. It also provides the benefits of mobile computing technology.
Flexibility
Users can access data from any device and from anywhere in the world. All they need is access to the web.
Real-time Data Availability
Data is updated almost instantly. Team members and team leaders have access to the most up-to-date and accurate information possible.
Disaster Recovery
With information stored on multiple physical data centers of the cloud provider, disaster recovery is easy and rapid. On the user end, disasters can occur in software or hardware. Regardless, cloud infrastructure offers quick redeployment of systems and data over the internet.
If the service itself has any disruption, users will be seamlessly routed to any available services provided by the vendor. This ensures business continuity and decreased user downtime.
Multiple Platform Support
Mobile cloud computing supports the use of multiple cloud platforms for development. Users aren’t tied down to a single cloud platform. This leads to greater agility for organisations. It allows developers to reach a larger market segment.
Cost Efficiency
MCC does not require a great upfront investment. IT upfront investment costs are nil. Hardware costs are reduced. Low-tier mobile devices will have the same access and availability as devices with higher-specs. This means organisations do not have to worry about increased user costs.
Typically, with cloud providers, service is pay-as-you-go. Businesses only pay for what they use. This model is also energy-efficient, further reducing costs.
Integrated Data
All of the data is stored and maintained on the same cloud architecture. This allows for quick integration of data points. The integrated data provides insight with accurate and real-time analytics. APIs allow for combined services that are not otherwise available. These allow a large number of applications to communicate with one another. These integrations can maximise productivity.
Mobile devices have lower performance compared to desktops. This is because mobile devices run on a limited power supply. This can severely limit the application performance of complex processes. The mobile app can offload the computations to the cloud platform for processing. Offloading enables the most humble devices to use any application available.
Computational Offloading

Mobile devices have lower performance compared to desktops. This is because mobile devices run on a limited power supply. This can severely limit the application performance of complex processes. The mobile app can offload the computations to the cloud platform for processing. Offloading enables the most humble devices to use any application available.
Challenges of a Mobile Cloud
While carrying many benefits, MCC as a concept also brings several challenges.
Low Bandwidth
Mobile devices connect to the internet wirelessly. This provides a never-ending challenge for providers since compared to wired network access, this can cause a substantial decrease in bandwidth.
Availability
Just like the mobile devices themselves, there is a high level of variety when it comes to mobile network access. Out-of-coverage regions, overcrowding in tight spots like public transportation, network outages, and building structures affect connectivity. What’s more, different wireless frequencies also affect network speeds.
There are several different operating systems available on mobile devices such as Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android. Additionally, there are many viable versions of each OS. Each one interacts with the networks through the Intelligent Radio Network Access (IRNA) technique. This means that while the different OS can connect, they are managed differently and performance will vary.
Battery-powered

Mobile devices are run daily on a limited supply of power. Application performance can be affected by devices in various power management modes. And many apps will increase power usage to maintain cloud connectivity. If a device runs out of power, all functionality ceases. Cloud applications need to be energy-efficient. The amount of power usage and the extent of performance decline depends on developer lead mobile optimisation.
Security
Wireless connections provide a larger amount of access for malicious attacks. Wireless connections encounter more loss of data than wired. This makes identifying and managing threats more complicated. Cloud availability means anyone can gain access if they can provide the necessary details. Even simple data such as private photos can be more easily hacked into via the cloud compared to local device storage.
Mobile Cloud Security Threats
MCC is associated with all the security challenges of cloud computing. However, MCC also has the challenge of solving those issues on top of the constraints inherent to mobile devices. The main constraint is limited resources available to deal with a problem. Security algorithms that protect cloud infrastructure are too complex for individual mobile devices.
Possible Threats
Phishing
Phishing has been around since email first came into common usage. But it has now moved onto text messaging (SMS) and apps like Facebook Messenger and Whatsapp.
Hackers use text messaging and websites that appear authentic to gain confidential information (remember, any http://www site can be safe or dangerous, but clues such as a correctly spelled URL with the right domain name, e.g., .org, .com or .net, can help you understand its authenticity). They can use this information to access cloud data. Individuals with high-level access can be easily discovered and targeted using these methods.
Mobile Malware
Specific malware can target mobile devices and their unique operating systems. Because of the less powerful security tools available to mobile users, devices are more susceptible to these attacks.
Public Wi-Fi
While out in public, many people have a habit of connecting to free public wi-fi. But these are unsecured networks. Hackers can more easily gain confidential information over public networks. Hackers sometimes set up fake public servers to glean users’ personal information.
Malicious Apps
While in the minority, some apps that users download contain malicious code. In addition to transmitting user data, these apps can be given permissions to fully control devices and monitor users in several ways. Even non-malicious apps may be collecting sensitive data unbeknown to the user. This is a potential disaster waiting to happen. When a legitimate service is attacked its collected user data is leaked.
Data Leaks
With local device caching, a user may accidentally upload data to an unsecured public cloud. Disgruntled employees can cause havoc by leaking private company data to the public. Or, valuable data can be given to competitors or other organisations with malicious intent.
Physical Data Centres

Mobile computing data is stored in multiple data centers. This has many data recovery benefits. However, there is also a greater number of people with potential access to private information. Cloud providers must maintain security measures to prevent access from unauthorised personnel. For the businesses using the service, this means they have no direct control over this access.
Security Considerations
While MCC adds layers of complexity to security, organisations can take proactive measures to reduce risk.
IT Experience
Businesses need to hire IT personnel with mobile security skills and cloud computing competence. IT must be available to direct all employees with mobile computing best practices and tutorials.
Maintain Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Management and IT must communicate and effectively educate all employees on mobile device SOPs. This includes the procedure for maintenance and updating device security, as well as the use of data loss prevention tools (DLP).
While ideally employees will have separate devices for business and personal use; this is often not the case. Companies can put best practices in place to deal with this by educating employees. This includes handling app installations and permissions.
Private Network Access
While working in the office, users have additional layers of cybersecurity including a firewall. However, the entire point of mobile computing is to allow users maximal flexibility. The business should provide company-wide access to a virtual private network (VPN). Employees increase data encryption when connected to the VPN.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Make MFA the company standard for all mobile app usage. This extra level of security prevents unauthorised cloud access with leaked or hacked credentials. MFA can also alert employees of failed login attempts which can be immediately reported to IT and management.
Limit Access
When it comes to connecting to the company network, IT should use control methods and limits. Requirements for device OS and version level will ensure employees have up-to-date mobile security. Third-party security tools can be required as necessary. By limiting access, organisations can ensure company-wide compliance and reduce potential security issues.
How RingCentral Supports Mobile Cloud Computing
At RingCentral, we provide solutions for all of your telecommunication and mobile communication needs. We give you the tools to work from anywhere on any device. Many apps and packages are available for small businesses or global enterprises.

RingCentral Phone for Mobile
A simple solution for small businesses is RingCentral Phone. Use your iPhone, iPad, or any Android device to take HD voice, fax, text, online meetings, and video conferencing needs. Take your smart device anywhere and stay connected. Whether you are in the office or at home, keep up to date with the RingCentral Desktop App.
Unified Business Communications
Carry your business anywhere you go. Use a company-provided device or your own personal smart device. Stay connected in one unified experience. In addition to HD VoIP capability, you can use real-time team messaging and file sharing with unlimited cloud storage.
Seamlessly switch between work phone, mobile, and desktop, enjoying a consistent performance and experience. The service is highly customisable and includes advanced call directing and recording. HD video conferencing can host up to 500 participants. Meeting features include direct dial-in and screen sharing.
RingCentral for Android
Android users can enjoy full capability and integrations by using the RingCentral Android mobile app. Use one business number for calling, faxing, and messaging. Manage your entire system on the go; you can even log in with your Google credentials.
Experience a quality and secure communications system. It features VoIP calls over wi-fi and customisable automated replies. HD audio and video technology auto-scales with bandwidth for optimal performance.
Connect to everyone in the company via the mobile app. Large or small, globally connect your workforce. You can increase security with the option to add and remove user access to data and contacts.
Host video meetings and audio conferences and invite through emails and messaging. Fax files from anywhere, using cloud storage or straight from the Android device.
Mobile cloud computing will take your business into the next wave of technology. Your large or small business can gain the benefit of maximal flexibility.
Contact RingCentral today to find out more.
Originally published Mar 02, 2021, updated Jun 19, 2021