What is cloud backup and why is it important to businesses?
Online businesses have seen exponential growth over the past decade, with more and more organisations joining the digital fold in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The internet has opened up unimaginable possibilities for businesses, helping them reach audiences and promote their products and services worldwide. Sadly, this exceptional growth phenomenon also has a flipside. Companies are now more vulnerable than ever to cybersecurity attacks.
That makes data backup even more crucial, and most businesses now rely on cloud backup.

This leads us to the question:
What is the cloud?
The cloud, or cloud computing, broadly refers to computing services provided over the internet.
Cloud computing is different from conventional web hosting. The services of cloud computing are sold on-demand and according to the need and usage of the customer. This pay-as-you-go service represents a shared platform for storing, managing, and processing data directly on the web.
Businesses across the board are rapidly moving to the cloud. Cloud computing helps eliminate the implementation and retention costs of an onsite IT infrastructure. Cloud services are completely managed by external service providers.
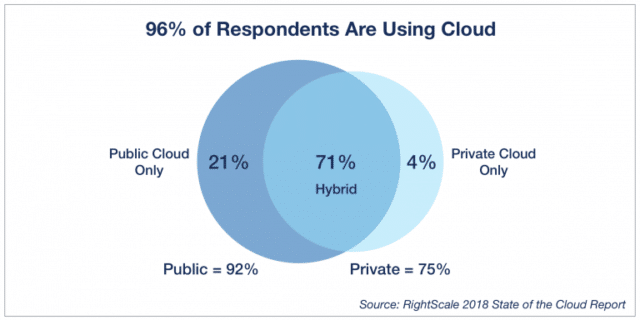
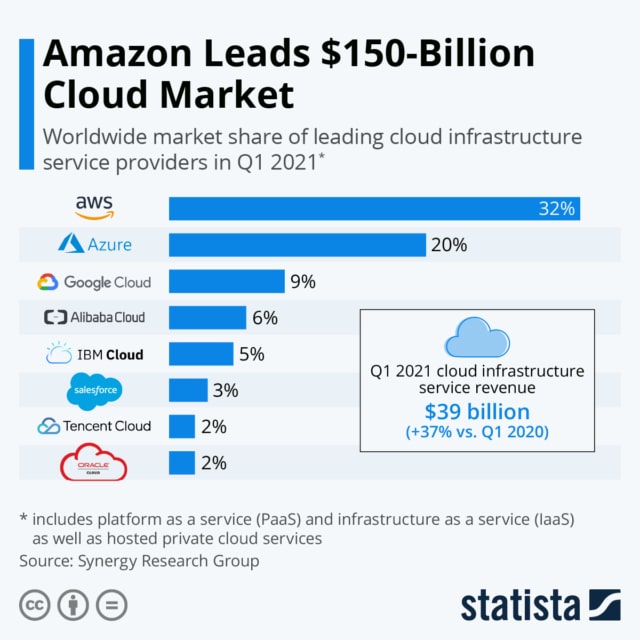
A cloud can be private or public. A public cloud offers services to everyone like the Amazon Web Service (AWS). A private cloud on the other hand, caters to a select group of users.
What is cloud backup?
In a nutshell, cloud backup is a method of data storage on an offsite location. What’s stored is a copy of critical files and data—think of it like a virtual external hard drive or NAS. The main purpose of a cloud backup service is to prevent data loss in case of a system failure or malware attack.
The offsite location usually refers to a secondary server or external data storage system. These are hosted by a cloud storage service provider which charges fees based on the services used by the backup customer.
These include the amount of storage space used, file size, number of devices, number of times the cloud is accessed, etc.
Cloud backups are now increasingly being used by medium and small businesses as well as bigger enterprises for effective data backup. Large companies use online backup services as an additional method of data backup.
Cloud backup helps boost a business’s data protection strategy without putting any additional strain on their in-house IT team.
How does a cloud backup work?
Cloud backup involves copying data onsite—I.e., in a company’s own data centre—and transferring it to a remote or offsite storage system to be easily accessed for disaster recovery (DR) purposes.
There are multiple ways of performing cloud backup. You can:
- Backup on the public cloud
- Backup to a service provider
- Cloud-to-cloud (C2C) backup
Backup on a public cloud involves sending data directly to cloud storage providers, such as Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS). First, the company selects the files to backup. Next, the files are encrypted and copied using the company’s own backup software and sent to the offsite cloud storage service.
It’s important to note that with backup on a public cloud, IT teams often need to implement additional data protection measures.
Backup to a service provider involves sending data to a designated cloud service provider that provides online backup services in a controlled data centre. The service provider may provide the backup software the company uses to send its data. Alternatively, the service may support specific commercial backup solutions.
Cloud-to-cloud (C2C) backup services copy data from one cloud to another cloud. The cloud-to-cloud backup service usually provides the software for this process.
Steps when adopting cloud backup
The following steps help efficiently adopt cloud backup:
- You purchase data storage from your chosen backup solution provider
- The software will then be installed in the IT ecosystem of your organisation
- You can choose which applications, files, and other important data to back up
You can start using your cloud backup system when the configuration is completed. Service providers usually allow you to set up a schedule for backup options, file syncing, controlling your allocated bandwidth, adding any important files if required, etc.
This is a mostly seamless process. Once your cloud backup service has been customised, you no longer have to worry about the backup process. All data is backed up automatically, with minimal input from IT teams.
More and more businesses are choosing to adopt cloud backup solutions for its easy and hassle-free deployment.
What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is a type of data storage which allows data to be stored, accessed, and managed in a third-party remote cloud server via the internet. Cloud storage is maintained by a designated cloud storage provider (Dropbox and Ondrive are perhaps the most well-known examples).
This service provider ensures that a user’s data is stored safely and easily accessible at all times.
Types of cloud storage
There are three main types of cloud storage:
1. Public cloud storage
This is a multi-user storage platform used mainly for storing less sensitive data. Public cloud storage acts as a universal data centre where the general public can store and access data via the internet.
2. Private cloud storage
Private cloud storage is devised and used exclusively by one company and can be managed both internally as well as by external service providers. Private clouds are generally used by businesses that require full control over their data and high security, as well as easy file sharing.
3. Hybrid cloud storage
Hybrid cloud storage uses a mix of public and private cloud storage. In the hybrid model, sensitive data is stored in the private cloud, while less sensitive data is stored in public cloud storage.
Cloud backup vs. cloud storage
The terms cloud storage and cloud backup are often used interchangeably, but there are important distinctions between the two.
Cloud storage is essentially a supplemental platform for on site storage. This stored data can be accessed by the users at any time and from anywhere over an internet connection.
Cloud backup on the other hand, is the backing up of data to an offsite location like a secondary server managed by a third-party cloud backup service provider. Cloud backup can be used to synchronise data between on-site systems and the cloud. So, any edits made to the on-site data will also get reflected in the cloud version.
Another key objective of cloud backup solutions is to ensure data protection and restoration in case of a security breach or systems failure.
In case the data is affected by ransomware or in the event of wrongly deleted files, business can continue as usual without being affected because of the copies of data stored on the cloud, removed from the physical system.
Types of cloud backup
There are three main types of cloud backup that users can choose from according to their specific needs:
Full backup
As the name suggests, a full backup copies the data source in its entirety each time you initiate backup. Naturally, this guarantees the highest level of data protection. On the flipside, full backups are time-consuming and push the storage limit. So understandably, this is not something that most companies can afford to do on a regular basis.
Incremental backup
Incremental backup is popular because of the limited resources it uses. It only backs up the data that has been modified or updated since the last backup. Unlike a full backup, this model saves time and storage space. However, it also makes a full restore more challenging.
Differential backup
This is similar to incremental backup because it backs up data that has been altered. However, differential backups back up data that has changed since the last full backup, rather than the last backup in general. This method solves the problem of difficult restores that can arise with incremental backups.
How is data restored?
Backups are made through a software application (maybe even a mobile app), usually provided by the cloud backup service provider. The software facilitates automated backups, following a preset schedule of the user’s instructions. For example, if you choose day-to-day backups, the software application will select, encrypt, and transfer your data to the service provider’s cloud servers on a 24-hour cycle.
The service provider may do incremental backups after a full initial backup to reduce bandwidth consumption.
The same cloud-based software application can restore data from the cloud backup. You can restore the entire backup or specific important files. Cloud backup facilitates data restorations from anywhere on any fixed or mobile device.
For example, if an organisation’s data centre has been compromised, it can restore data directly at the remote disaster recovery (DR) site.

Advantages of cloud backup
The size of the global cloud backup market is estimated to reach a staggering $4229.3 million by 2026. Here are some of the advantages of adopting cloud backup for your business:
It’s cost-efficient and cheaper compared to maintaining an in-house backup operation
With so many options to choose from, it is easy to find a backup solution that is reasonable in terms of pricing, yet effective. Also, it’s a more economical option than setting up and maintaining an in-house backup service, especially for small businesses.
It’s scalable and can adjust according to business needs
One of the biggest advantages of cloud backup is that it can be scaled up or down depending on the specific growth trajectory of your business. You can simply ask your service provider to increase or reduce the amount of disk space or processors allocated to you, eliminating unnecessary costs.
It can be easily set up and accessed anywhere on-demand
Another reason cloud backup is a smart choice for businesses is that it can be accessed from anywhere and at any time as long as you have access to an internet connection. Conduct business on the go from any number of devices including your Mac (via MacOS, iPhone (via iOS, iPad, and other mobile devices (via Android).
It provides advanced and resilient security against cyber attacks
Storing critical data at a remote location ensures its safety in case of on-site data breach or system damage. The best cloud backup services provide high-level security and data protection.
Challenges of cloud backup
In spite of its many advantages, cloud backup also poses a few challenges:
Its performance can rely on your bandwidth and latency
Data transfer relies on network connectivity and the distance between sites. To ensure a quick and seamless data transfer from the production site to the cloud backup storage, you need sufficient bandwidth. Not all businesses can afford large bandwidth capacities.
Unreliable cloud backup providers run the risk of massive data corruption
It’s always advisable to find a reputable backup service provider since unreliable vendors present the risk of data corruption.
Costs may go higher depending on the volume of data backed up on the cloud
An obvious disadvantage of cloud backup is that costs can and do go up when backing up large volumes of data.

Important qualities to note when looking for a cloud backup provider
- An easy and straightforward method of operation
- Simple and convenient to deploy
- Intuitive and user friendly interface
- Scalable
- It should comply with all security regulations (GDPR, etc.) and hold relevant security certificates (I.e., SSL)
- It should have a data archiving feature
Cloud backup best practices
Research & study cloud backup providers
The top five cloud backup providers for 2021 are: Backblaze, iDrive, Carbonite, Acronis True Image, and CrashPlan. While Backblaze offers unlimited storage and lets you back up files from both Windows PC and Mac, iDrive also supports Linux. Choose the option that best suits your needs.
Conduct intermittent tests on the backup and data recovery
Test your backup strategies and data recovery to ensure they’re equipped to deal with a disaster.
Make your data restoring system as accessible as possible
Choose a data restore destination that is easily accessible and does not overwrite existing data.
Have a system of deciding the significance of files to back up
Decide on the specific data to back up based on the criticality of the information to business operations.
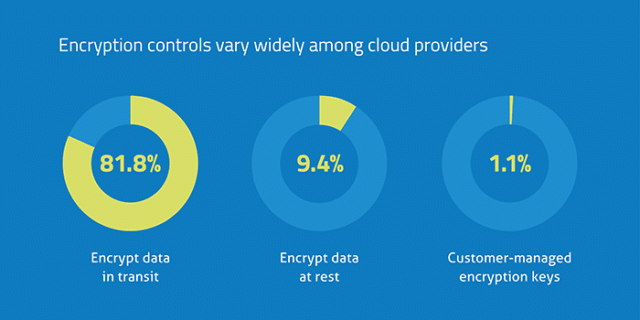
Use private encryption for confidential data
It’s good practice to use private encryption for data that you want to keep confidential.
Does your business have a secure cloud backup system?
There are multiple choices when looking for a secure cloud backup system for your business. Remember to do your research first and choose a vendor that provides backup solutions which meet your specific business needs.
Don’t rest on your laurels once you’ve got cloud backup established, though. Solutions like your business communications platform still need to take cybersecurity seriously.
Originally published Oct 05, 2021

