The word “chatbot” is familiar to most of us, but what does it really mean? Well, a chatbot is simply a computer programme that you can have a conversation with.
Today’s chatbots are able to understand human language better than ever, and that represents a huge opportunity in business communication. From customer support to data analytics, bots can save you both time and money by making your services more efficient.
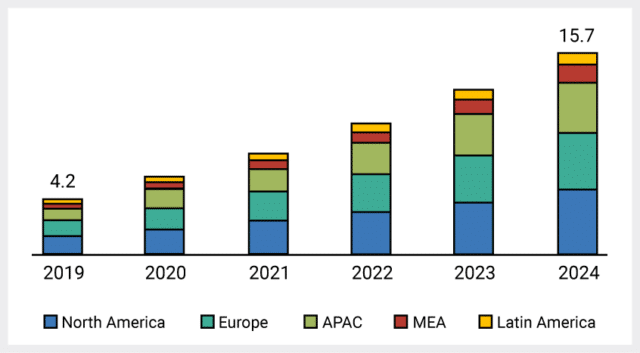
It’s predicted that 85 per cent of customer interaction will be handled without human agents by 2021, and the global conversational AI market size is expected to grow from $4.8 billion in 2020 to $13.9 billion by 2025 (as shown below).
This doesn’t mean that humans are no longer required, however! Chatbot technology does have its limitations, and bots are best suited to handling simple tasks and frequently-asked questions.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at exactly how deep learning and machine learning chatbots work, and how you can use them to streamline and grow your business.
Types Of Chatbot
First, let’s consider the different types of chatbot. When we think about robots, we often picture them having “bodies”, but in most cases they are basic computer programmes that allow users to interact with a website or app.
Chatbots can be divided into two broad categories: rule-based chatbots, which complete scripted actions based on keywords, and AI-powered chatbots that use machine learning in order to make their conversation sound more human.
Rule-based chatbots are the simplest form. They have been programmed to recognise common words and phrases, and to provide standard answers to popular questions. Their responses are based on a keyword or phrase typed in by the user.
For example, they could answer FAQs about store opening times or delivery charges—but they wouldn’t be able to answer a more in-depth enquiry, or one that uses words not found in their dataset.
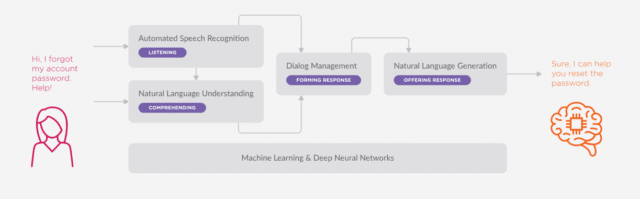
Artificial intelligence chatbots appear more human-like in their abilities. Because they use machine learning to develop their language skills, they are capable of remembering the things people say to them and recalling the information for future interactions.
They are still programmed to send back certain messages in response to certain questions, but their responses are more flexible and feel more like a human conversation.
Introducing Machine Learning Chatbots
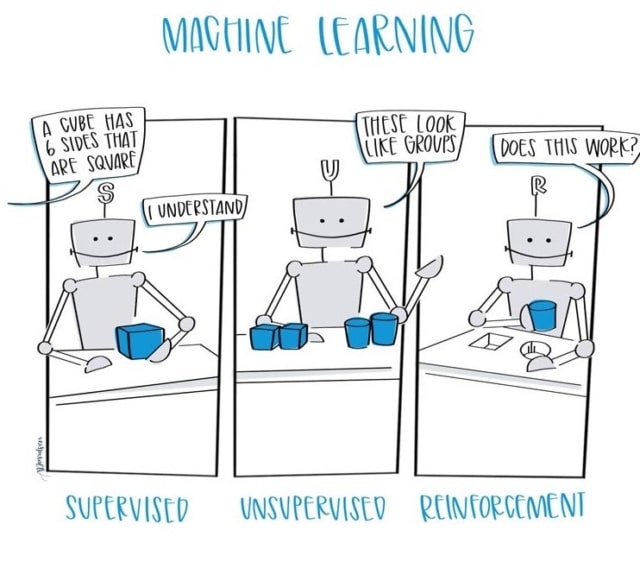
Machine learning refers to the way computers can be taught to behave more like the human brain. It uses training data and natural language processing (NLP) to teach machines to solve problems, answer questions and draw conclusions without human intervention.
Basically, AI units (including chatbots) can learn how to make human-like conversation by studying algorithms and conversational inferences. The more they hear, the smarter they become.
And once they know how to do it, they can learn new things and make inferences all by themselves—even handling questions they haven’t been specifically programmed to answer.
People often think this sounds a bit scary, with robots listening in on our conversations and growing more intelligent every day. But the humans are still very much in charge, directing the bots’ development and harnessing the limitless possibilities to improve our lives.
Genuine artificial intelligence means a chatbot must not only be able to offer an informative answer and maintain the context of the dialogue—it must also be indistinguishable from a human. But for the moment, most people are aware that they’re talking to a chatbot, no matter how clever it is.
Everyday Applications
Many of us will be using chatbots already, even if we don’t always realise it. For example, it’s estimated that nearly a quarter of the world’s population was using chatbots by the end of last year.
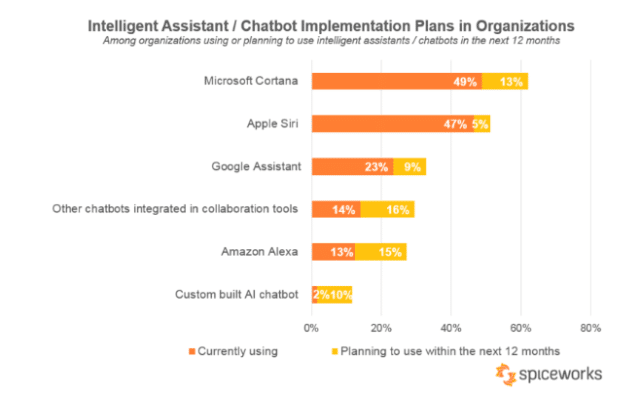
There are two main types of dialogue system. Goal-oriented chatbots like Siri help users achieve predefined goals and solve everyday problems using natural language, while advanced conversational AI aims to create a more sophisticated chatbot experience.
You’ll definitely have seen chatbots pop up when you visit a website’s landing page, asking if you need help with anything. These are usually programmed to answer basic queries and suggest solutions, and in some cases they are capable of passing you through to a human agent.
Chatbots often communicate in writing, such as the automated messaging service used by Facebook Messenger. People also interact with them via voice commands—if you use virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri or Amazon’s Alexa, then you’re conversing with a bot.

And of course, we’ll all have encountered chatbots (sometimes called conversational agents) when we contact a company’s call centre.
In business, the use of chatbots is rising fast—which isn’t surprising, given the number of applications for the technology. For instance, chatbots can help online customers find what they’re looking for, answer FAQs, and walk them through the payment process.
They can also enhance the customer support you offer, as they’re available 24/7. This is especially true if you harness deep learning technology, which we’ll look at in the next section.
What is a Deep Learning Chatbot?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning where numerous layers of algorithms are created, each providing a different interpretation to the data. These are known as artificial neural networks, which aim to replicate the function of neural networks in the human brain.
A deep learning chatbot learns everything from data based on human-to-human dialogue. The more data you feed in, the more effective its learning will be. Training chatbots as thoroughly as possible will improve their accuracy.
The two main types of deep learning chatbot are retrieval-based and generative. Retrieval-based chatbots have a “repository” of responses they can draw on to answer queries—whereas the more advanced generative chatbots don’t use a predefined repository.
Deep learning chatbots can be trained using existing interactions between customers and support staff; preferably as detailed and varied as possible. The training process also includes data reshaping (creating message-response pairs that the machine will recognise) and pre-processing (adding grammar so that the chatbot can understand errors correctly).
This type of chatbot also uses “word vectors” to recognise the semantics of a word rather than just the word itself (see example below). This gives them the ability to analyse relationships across words, sentences, and documents, and enables things like speech recognition and machine translation.
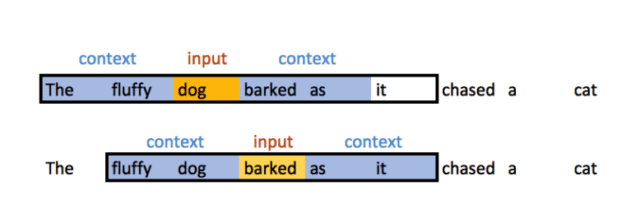
Word2vec is a popular technique for natural language processing, helping the chatbot detect synonymous words or suggest additional words for a partial sentence. Coding tools such as Python and TensorFlow can help you create and train a deep learning chatbot.
Many businesses use GitHub, a web and cloud-based service that allows developers access to public and open-source codes and provides community support to coders.
You can use it to learn Artificial Intelligence Markup Language in order to programme natural language software agents such as chatbots. For example, RingCentral’s Glip app lets you build your own bot using GitHub repositories.
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
This can be a tricky one to understand, because deep learning is essentially an evolution of machine learning. But deep learning requires much more data than machine learning, and the difference lies in the way data is presented to the system.
Machine learning algorithms require structured data to learn from, and can make informed decisions based on what they have learned.
Deep learning structures the algorithms in layers, to create an artificial neural network that can learn and make intelligent decisions by itself.
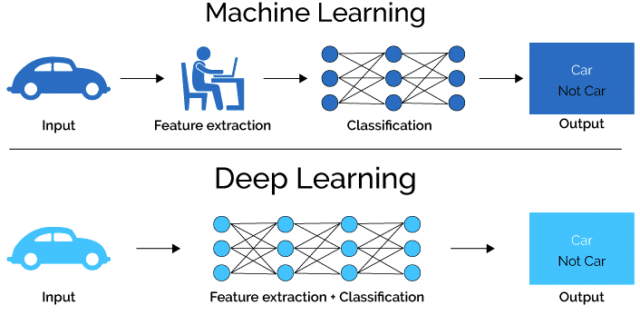
Machine learning networks sometimes need guidance from humans when they get things wrong. Deep learning networks do not usually require human intervention, as they are capable of realising when they’ve made an error and learning from it.
Machine learning is suitable for your business if your data can be structured and used to train the algorithms, in order to automate some of your basic operations.
Businesses that require computers to solve more complex queries—and have a ton of data to help them learn—could take advantage of deep learning.
How Chatbots Can Be Used for Business
Artificial intelligence has myriad applications for businesses, from speeding up customer response times to automating systems. We’ve picked out a few examples of how you can use chatbots to your advantage.
1# Improved customer support.
There’s no question that your human customer service team is vitally important to your business. There are plenty of times when a human touch still is required. However, there are also times when problems or enquiries can be resolved more quickly and efficiently by a chatbot.
The main thing is to recognise when a chatbot can get the job done, and when a real agent needs to step in. If possible, customers should be given the choice of whether they speak to a human or a bot—and you should never attempt to pass off a chatbot as a person!
We’ve all heard people complain about robots answering the phone in call centres (“Press one for accounts, two for customer service. . . you are number 456 in the queue”). However, as long as the query gets resolved, customers won’t mind who (or what) dealt with it.
In fact, 40 per cent of buyers don’t care if they are served by a bot or a human agent, as long as they get the support they need. The key is to integrate chatbots with humans—make sure the bots know when to pass on an enquiry, and the humans know which tasks can be automated.
#2 Faster response times.
Customers in a hurry will be especially happy to interact with a chatbot online, instead of having to contact your call centre or wait for a human to send an email response.
Email and text responses can also be handled by chatbots—for example, they can be programmed to send a generic (or even personalised) response telling the customer you’ve received their enquiry and are working on it.
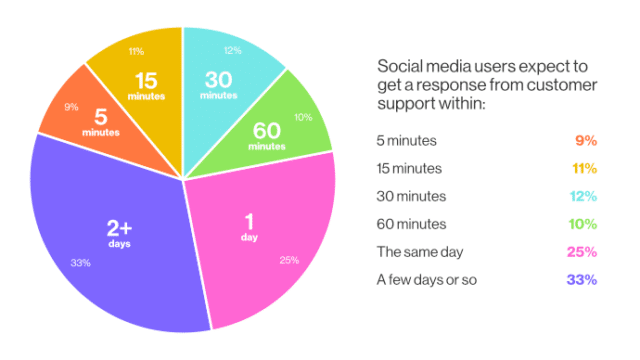
This works for social media messaging, too. Instant responses are very important to social media users, especially millennials, so chatbots can be used to generate replies and answer FAQs.
#3 More efficient administration.
This is an area where chatbots can really help to streamline your business. Because they can be programmed to handle mundane functions, your human employees will be free to get on with other work—thus improving productivity and saving money.
For example, RingCentral’s free Glip app comes with a chatbot assistant that can perform simple tasks, automate workflows and help you interpret data.
While robots are not about to replace human staff completely—and we wouldn’t want them to—they can help small businesses operate with smaller teams, and from smaller premises since digital agents don’t need office furniture.
Another advantage is that chatbots work 24/7 without expecting a pay packet to match. Businesses won’t have to pay staff to work through the night, as a chatbot can deal with queries outside of normal working hours—and those interactions can always be followed up later when the humans are back at their desks.
#4 Detailed analytics.
Chatbots are a great tool for helping businesses learn more about the needs of their clients and adjust their customer service strategies accordingly.
In most cases they are able to record, store, process and retrieve customer data more efficiently than a human could, and can provide detailed analysis of trends and behaviours.
This information will give you a better understanding of your customer base, and help you work out ways to target the right clients, with the right products, at the right time.
#5 Options for personalisation.
Understanding your customers’ needs, and providing bespoke solutions, is an ideal way to increase customer happiness and loyalty.
Although some are wary of companies collecting and using their personal data, most people are pleased when a business remembers their preferences and offers them products and discounts based on previous choices.
Ecommerce sites often show customers personalised offers, and companies send out marketing messages with targeted deals they know the customer will love—for instance, a special discount on their birthday.
This kind of personalisation can be achieved by using chatbots, which monitor customers’ preferences and automatically suggest the most relevant products.
On-demand streaming services also use machine learning to recommend new songs, movies or TV shows to users based on their choices. The algorithms also associate their preferences with those of other users who have similar tastes.
Current Drawbacks
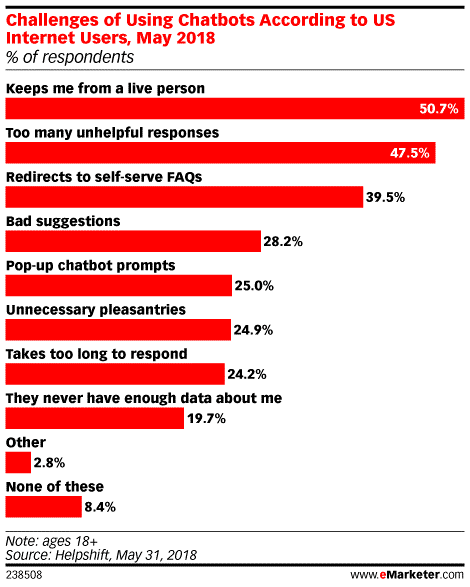
There’s a temptation to hail artificial intelligence as the key to a utopian future, but we’re not quite there yet. NLP technology is still in its infancy, and chatbots are far from flawless.
While chatbots can play an increasingly human part in business, it’s important to recognise that they do have limitations. They can only be programmed with a finite set of answers and responses, and they can’t always ask extra questions if clarification is required.
Although analytics can be automated for maximum efficiency, a human eye is still useful in interpreting data and customer feedback, and acting upon it. And if your company doesn’t have enough data to feed and train the chatbot, it won’t perform as well as you’d hoped.
Another thorny issue is that of data protection—chatbots need data to learn from in order to personalise the user experience, but strict regulations can make this more difficult to achieve.
What the Future Holds
Although nobody knows for certain what the future holds, it’s pretty clear that chatbots development will continue its rise—and that they’ll keep getting smarter.
47 per cent of organisations are expected to implement chatbots for customer support services, and 40 per cent are expected to adopt virtual assistants.
Predictions include a particular increase in the use of voice-activated chatbots alongside the written interactions. As the technology improves, there will be more strides towards conversational AI.
We can also expect to see chatbots used for automating payments, giving customers the ability to pay directly via live chat or social media messaging, while personalised shopping with chatbots is also likely to increase.
One study estimates that chatbots will save businesses over $8 billion per year by 2022.
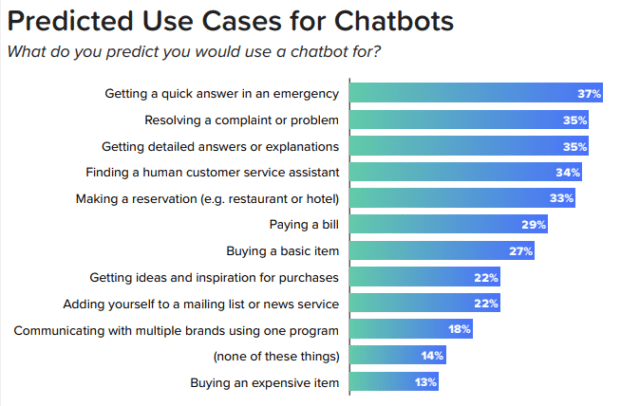
Conclusion
If you’re considering using machine learning or deep learning chatbots for your business, make sure you do some detailed research both internally and externally. It’s a good idea to discuss the pros and cons with your employees to work out exactly how the technology could benefit your business.
The bottom line is that you should only use chatbots if the concept is a good fit for your business, and can be trusted not to alienate or annoy your customers. You don’t want to sacrifice the customer experience on the altar of progress.
Originally published Jan 26, 2021, updated Dec 14, 2023
