In this article, we’ll cover:
DSL: A quick definition
The high-speed internet that you connect to via Wi-Fi or an ethernet cable through a modem is DSL internet. DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line/Loop and it is a communication medium that receives data via a copper telephone landline. (If you’ve stumbled on this page while trying to learn about domain specific languages, another phrase sometimes known as DSL, it’s time to bow out).
DSL is the primary form of broadband internet access and uses existing telephone wiring to transmit data via a DSL modem, making the internet accessible to all.
There are three types of DSL (collectively summarised as xDSL):
- ADSL: Asymmetric DSL provides faster download speeds. Receiving data is faster than sending data. Download speeds up to 20 Mbps and Upload up to 1.4 Mbps.
- SDSL: Symmetric DSL splits the incoming and outgoing frequencies equally, so upload and download bitrates are the same.
- VDSL: Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line. This is an upgrade on the prior HDSL, VDSL connects to extremely high frequencies providing download speeds of up to 52 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 16 Mbps. VDSL2 can provide speeds up to 100Mbps for both upload and download.
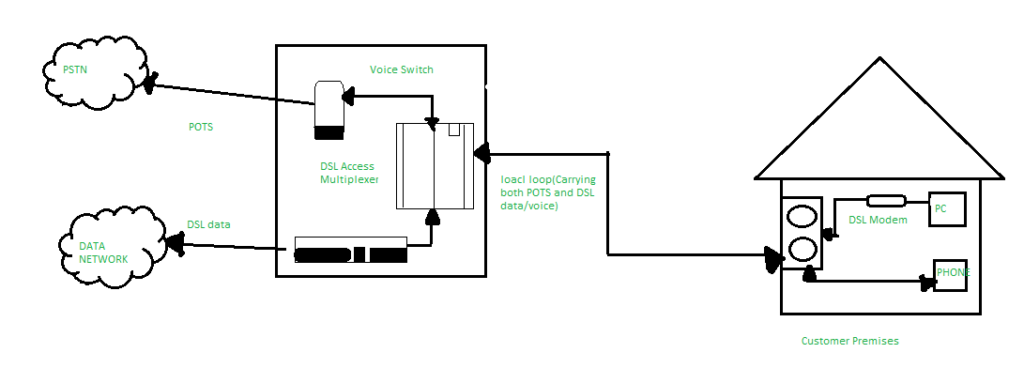
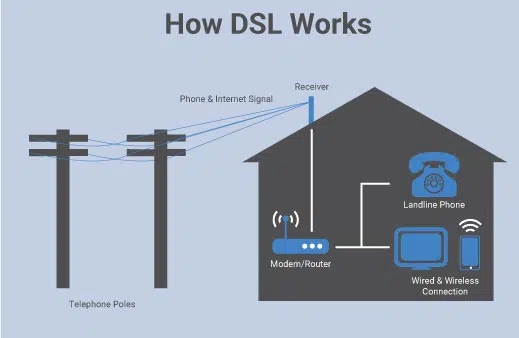
How does DSL work?
A DSL modem receives signals via telephone lines and converts them digitally for your use. This data can be transferred to you wirelessly or via an ethernet cable. The use of existing telephone lines makes DSL accessible in rural areas as well as towns and cities. Phone lines have a higher capacity than required by phone calls, so DSL signals can easily piggyback across the same infrastructure.
The DSL modem or router is a standalone device that can connect to multiple computers or mobile devices. DSL technology does not interfere with your landline phone service because of different operating frequencies. Phone and internet systems can function simultaneously.
DSL is a cost-effective method to connect to the internet with high-speed bandwidth, as compared to cellular data. It’s much faster than a dial-up connection with a high bitrate. DSL speeds vary from 256 Kbps to 100 Mbps. Internet providers have various packages depending on the connection speed you need.
With businesses embracing the cloud, uploads and downloads from the cloud are constant and require high-speed internet access. While DSL is a good option, there are more options one could explore.
DSL vs cable
Structure
Cable internet is a type of broadband internet connection that uses coaxial cables to connect you to the internet. It uses the same infrastructure as cable television, quite analogous to a DSL service using telephone lines. Cable internet is popular among residential users and one of the cheaper options.
Availability
Cable internet is almost as easily available as DSL. It’s widely accessible because of the reach of cable television, especially in urban and suburban areas. You can easily find packages bundled with your cable TV monthly subscription.
There might be availability issues in rural areas. DSL comes to the rescue there because telephone lines have reached where cable still has not.
Reliability
Speed reliability can be a concern with cable internet. Cable internet uses a shared network and the coaxial cables are susceptible to network congestion. This can lead to slowed speeds and performance can dip during peak times.
Speed
It’s among the fastest internet types out there. Download speeds can go up to 1 Gbps and upload up to 50 Mbps.

DSL vs fixed wireless internet
Structure
Fixed wireless internet is a good option for rural and underserved areas that do not have telephone lines or cable TV. The internet is broadcasted through towers. Imagine a wireless modem for a whole town. Airwaves from the towers transmit data to receivers in a user’s property. Ideally, the distance from the tower to the receiver is 10 miles. There has to be a line of sight between the tower‘s access point and the receiver.
This is a particularly great option to provide high-speed broadband to far-flung areas with little or no access to telephone line networks. It tends to be more expensive than DSL. It’s easier to set up fixed wireless internet, though, because it doesn’t require physical cables.
Availability
Fixed wireless internet is a solution to provide internet in areas without telephone infrastructure. Its availability would be dependent on a local business investing in creating the required infrastructure. Fixed wireless internet is not usually owned by big telephone providers. This makes it a little more expensive and less adaptive than other internet options.
Fixed wireless internet has always been an option for rural areas but lately, some urban providers are using it to provide internet to entire apartment complexes.
Reliability
Fixed wireless service is mostly reliable. Since the connection is made via airwaves, a line of sight is required, so your connection could be disturbed by buildings and other objects in the way. Rain, fog, and other weather conditions can deteriorate the signal strength and thus functionality.
Speed
Its speed is comparable with DSL internet service if not faster, from 5Mbps to 50 Mbps. You can use fixed wireless internet for streaming videos, sending large files over the internet, and using numerous other web-based tools. Because there can be many intrusions to the signal, due to weather, etc., speed may vary.
Also, providers offer generous data caps as compared to DSL providers.
DSL vs fibre optic internet
Structure
Arguably the best internet connection there is, is fibre optic internet. Internet data is transmitted to your home via a fibre optic cable. These cables have thin strands of glass or plastic and signals are transmitted as pulses of light.
Pulses carry binary data, just like everything over the internet. One pulse means one and no pulse means zero. This results in unimaginably fast connections and that distances, long or short, are of no concern.
Naturally, as all good things in life are, this is perhaps the most expensive of all our internet options. It has recently become more competitively priced, but if you consider the speed of the internet it provides, it turns out to be a cost-effective way to connect to the internet.
Fibre optic internet has a large bandwidth, which means it can accommodate growing populations and use of the public internet cloud.
Availability
Availability depends on if you have a service provider who has gone through the trouble of laying fibre optic cables around your town or city. It’s a massive logistical challenge, not to mention the nuisances of competition and the red tape they have to cut through. Currently, big service providers have limited fibre optics in urban areas. If your home or central office is in a big city, you have the best chance of fibre optic internet being available.
Reliability
Reliability is superior to all other internet connection types. The signal is reliable and constant, even at distance. There are optical amplifiers that are used to amplify the signal when data is transported over thousands of miles. Copper cabling or telephone wires have higher attenuation and this affects the signal
Speed
The speed of fibre optic cables is naturally second to none. Download speeds can be as fast as 2 Gbps, which means you can download a 2-hour movie in under a minute. Upload speeds are also significantly faster than other types of internet connections.
Speed is consistently fast and you won’t expect a reduction in speed because of any interference or intrusion due to network congestion.

How to determine the right internet connection for you
The internet connection you choose will be dependent on several variables, some in your control and some that aren’t:
- The connections offered in your area will depend on a rural or urban setting
- The internet service providers (ISPs) active in your area
- Your budget
- Your internet needs. Depending on if you need to use the internet for work, online learning, or streaming movies.
- Your data cap. Large businesses process thousands of GBs of data every day and thus have different requirements than small businesses.
- Installation and equipment costs
- Overage fees
If you have a large or middle-sized business, you need to be mindful of the shortcomings of every technology depending on your company goals. Fast, reliable internet seems like a basic human necessity in the 21st century but how fast and how reliable you need it to be, changes from organisation to organisation.
If you use the internet for VoIP calls and video conferencing, you would need faster speeds than a business that uses landlines for all calls.
When evaluating your speed needs, you should also ask yourself how often you stream movies or TV shows. And how many people in your home use the internet for meetings, gaming, streaming, etc?
If you have people studying and working from home, you would need fast upload speeds, too, especially for video meetings. Smart home devices can eat up bandwidth as well, so consider those.
Also, it’s vital to realise that the speed advertised by your ISP is not the speed you’ll get. When comparing different service providers and their plans, make sure you know what speed you are realistically receiving. Another way to gauge the speed of an ISP is to look at the bandwidth of your ISP. Bandwidth is the volume of information per unit of time that the ISP can sustain.
If you have the kind of business that cannot handle interruptions, consider an ISP that offers a Service Level Agreement (SLA). An SLA provides a minimum level of service, guaranteed at all times, it’s a service contract that tells you about the reliability of the internet connection.
A stable internet connection can easily be compromised because of a physical fault in hardware or a physically damaged line. Consider an ISP that has excellent customer service, can help you get up and running, and understands the importance of uninterrupted connectivity.
Choosing the right internet connection can prove to be the most important decision related to the connectivity of your home or business. You want to choose one that gives fast speeds with reasonable pricing. Weigh the pros and cons of each type of internet connection carefully and make a well-informed decision after carefully determining your internet requirements.
Many people opt for a DSL connection because it’s widely available. Fibre optic is mostly available in urban areas and tech hubs. Cable internet is also available but not preferred to DSL because DSL is more dependable. It’s hard to give the broadband crown to DSL or cable because while DSL can be easier on the pocket, cable can be faster.
Depending on what’s offered where you live, fast reliable internet is easily achievable these days. Between DSL, cable internet, fixed wireless internet, and fibre optic, you have the option to find the perfect internet connection for your home or business. Just do your homework before taking the plunge.
Originally published Feb 13, 2023